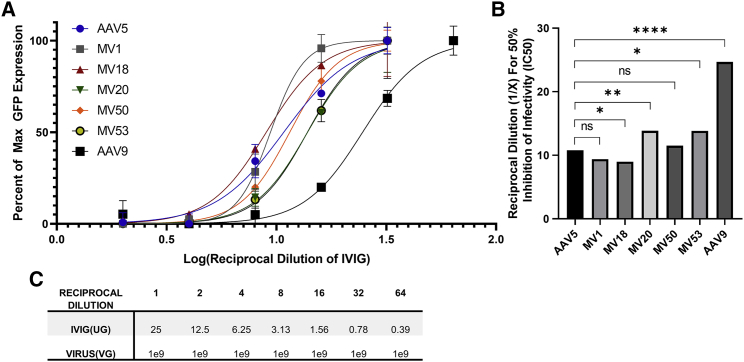
Figure 5.
Seroreactivity of AAV5 and MV Mutants using an IVIG-Based Assay
(A) AAV neutralization assay using pooled human immunoglobulins from thousands of donors (IVIG Carimune NF, ZLB Behring) to assess seroreactivity. MV mutants were compared to AAV5 and AAV9 in their ability to resist neutralization by IVIG. Each capsid serotype containing sc-GFP was incubated with reciprocal dilutions of IVIG and added to Huh7 cells. After 72 h, the GFP expression for each reciprocal dilution was quantified and compared to GFP expression of an infection control without the presence of IVIG. The percentage of max GFP expression at each reciprocal dilution for each virus was used to generate curves that represented the seroreactivity of each virus. Graphpad Prism 8 was used to curve fit the data. Serotypes with curves further to the right indicate less IVIG is needed to neutralize the virus. Serotypes with curves further to the left indicate more IVIG is needed to neutralize the virus. Plotted data points are shown as mean values ± SD. (B) Reciprocal dilution at which 50% inhibition is achieved was calculated from the best fit curves for each capsid. Extra sum of squares F test was used to compare the best fit curves for each capsid and determine whether one capsid is more/less seroreactive compared to AAV5. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (C) Approximate amounts of IVIG and virus used for each reciprocal dilution.