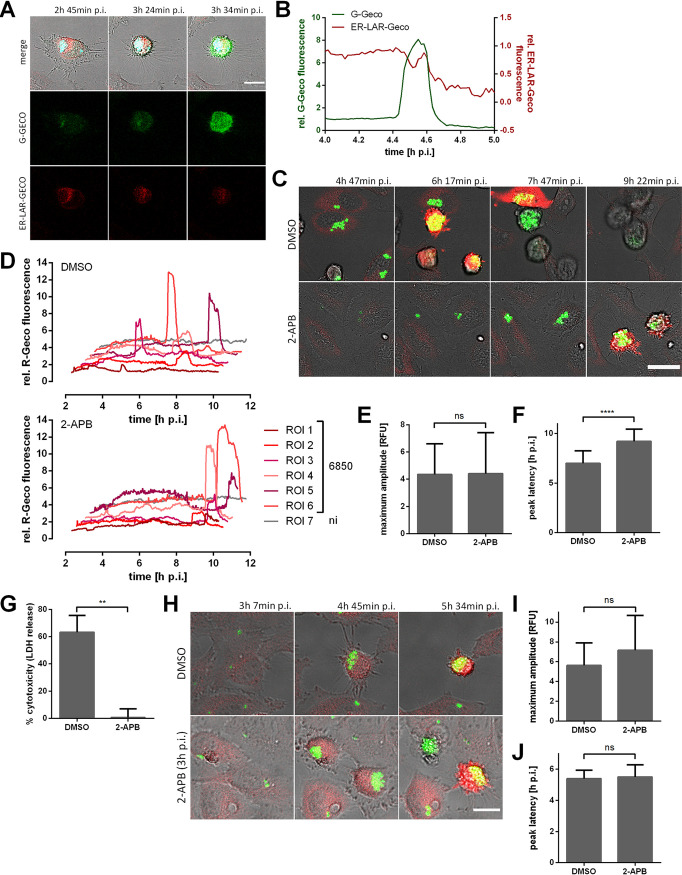
FIG 5.
Intracellular S. aureus modulates endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+ concentration. (A, B) HeLa ER-LAR-Geco G-Geco cells were infected with S. aureus 6850 Cerulean, and changes in ER and cytosolic Ca2+ concentration were monitored by live cell imaging. (A) Representative stills from time-lapse fluorescence microscopy (cyan, S. aureus; red, ER-LAR-Geco; green, G-Geco; gray, brightfield). Bar, 20 μm. (B) Relative quantification of Ca2+ concentrations in the cytosol and ER of a single infected cell. (C to F) HeLa R-Geco cells were treated with 30 μM 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate (2-APB) or DMSO as a solvent control 1 h prior to infection with S. aureus 6850 GFP, and R-Geco fluorescence was measured by time-lapse imaging. (C) Representative stills from time-lapse fluorescence microscopy (green, S. aureus; red, R-Geco; gray, brightfield). Bar, 30 μm. (D) Relative R-Geco fluorescence of single infected (6850) or uninfected (ni) cells was quantified over the time course of infection under the different conditions. (E) The peak amplitude of the relative R-Geco fluorescence of 27 to 32 single infected cells was quantified upon DMSO or 30 μM 2-APB treatment. (F) The latency of the relative R-Geco fluorescence peak after S. aureus intracellular infection was determined, and the mean value of 27 to 32 cells was calculated. (G) HeLa cells were treated with 30 μM 2-APB or DMSO as a solvent control 1 h prior to infection with S. aureus 6850, and cell death was determined at 6 h p.i. by LDH quantification. (H to J) HeLa R-Geco cells were infected with S. aureus 6850 GFP, and R-Geco fluorescence was measured by time-lapse imaging. At 3 h 7 min p.i., DMSO or 30 μM 2-APB were added. (H) Representative stills from time-lapse fluorescence microscopy (green, S. aureus; red, R-Geco; gray, brightfield). Bar, 20 μm. (I) The peak amplitude of the relative R-Geco fluorescence of 7 to 11 single infected cells was quantified after DMSO or 30 μM 2-APB treatment. (J) The latency of the relative R-Geco fluorescence peak after S. aureus intracellular infection was determined, and the mean value of 7 to 11 cells was calculated. Statistical analysis was performed by unpaired t test (**, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001).