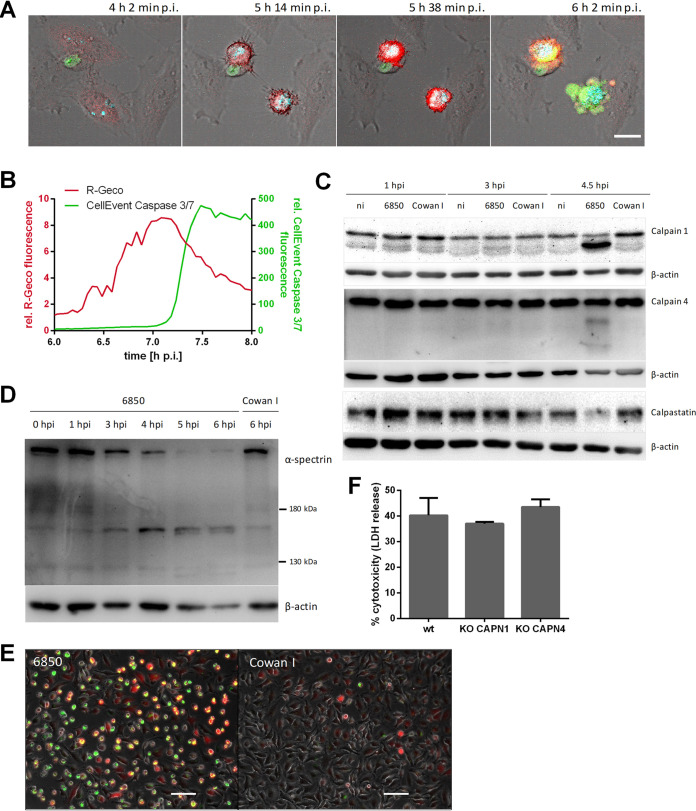
FIG 7.
Activation of effector caspases and calpains in S. aureus-infected cells. (A, B) HeLa R-Geco cells were infected with S. aureus 6850 Cerulean and CellEvent caspase-3/7 green detection reagent was added prior to live cell imaging. (A) Representative stills from time-lapse imaging are shown (cyan, S. aureus; red, R-Geco; green, CellEvent caspase 3/7; gray, brightfield). Bar, 20 μm. (B) The relative R-Geco and CellEvent caspase 3/7 fluorescence of a single S. aureus 6850-infected cell was quantified over time. (C) HeLa cells were infected with S. aureus 6850 or the noncytotoxic strain Cowan 1 or remained uninfected (ni), and cell lysates were prepared at 1, 3, and 4.5 h p.i. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred onto a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane. Protein abundance and/or cleavage of calpain 1, calpain 4, calpastatin, and β-actin as a loading control was detected using the specific antibodies. (D) Immunoblot assay was performed as described for panel C. S. aureus 6850- or Cowan 1-infected cells were lysed at 0, 1, 3, 4, 5, and 6 h p.i. Calpain-specific cleavage of α-spectrin (150 and 145 kDa) was detected by application of an anti-α-spectrin antibody with anti-β-actin antibody as a loading control. (E) HeLa cells were loaded with a fluorogenic calpain substrate (Boc-Leu-Met-CMAC) after infection with S. aureus 6850 or Cowan 1. The presence of activated calpains was detected at 4.5 h p.i. by fluorescence microscopy (red, Boc-Leu-Met-CMAC; green, S. aureus; gray, phase contrast). Bar, 100 μm. (F) LDH release of HAP1 wild type (wt), CAPN4 knockout (KO), or CAPN1 KO cells infected with S. aureus was determined at 6 h p.i. (n = 2). Statistical analysis was performed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).