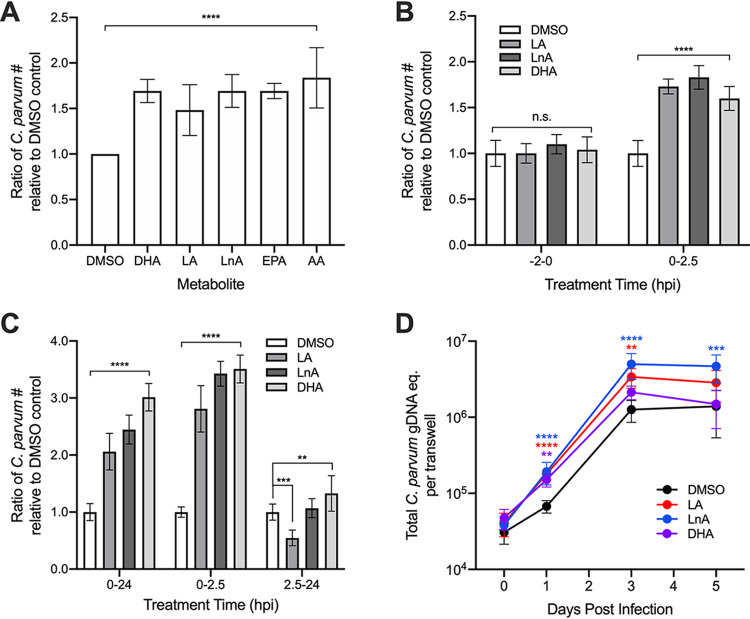
FIG 4.
Enhancement of parasite growth and invasion by metabolites and related molecules. (A) Average ratio of C. parvum parasites 24 hpi in treated samples relative to DMSO controls for the metabolites docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), linoleic acid (LA), and linolenic acid (LnA) and the related compounds eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and arachidonic acid (AA). (B) Samples were infected with filtered C. parvum sporozoites and washed after a 2.5-h incubation. Average ratio of attached C. parvum parasites relative to DMSO controls compared between samples that were pretreated with metabolites for 2 h and samples with metabolites added immediately after infection. (C) Average ratio of C. parvum parasites relative to DMSO control in samples infected with filtered sporozoites and treated with metabolites during invasion (0 to 2.5 hpi), after invasion (2.5 to 24 hpi), and for the duration of the experiment (0 to 24 hpi). (D) Effects of metabolite treatment on C. parvum growth in air-liquid interface (ALI) culture determined by the average total C. parvum genomic DNA (gDNA) equivalent per transwell on days 0, 1, 3, and 5 postinfection. DHA and AA were tested at a final concentration of 0.1 mM, and all other metabolites were tested at a final concentration of 0.5 mM. All data represent combined mean ± SD of three independent experiments, with 2 to 3 technical replicates per experiment, and were analyzed with a two-way ANOVA followed by a Dunnett’s test for multiple comparisons. **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001; n.s., not significant.