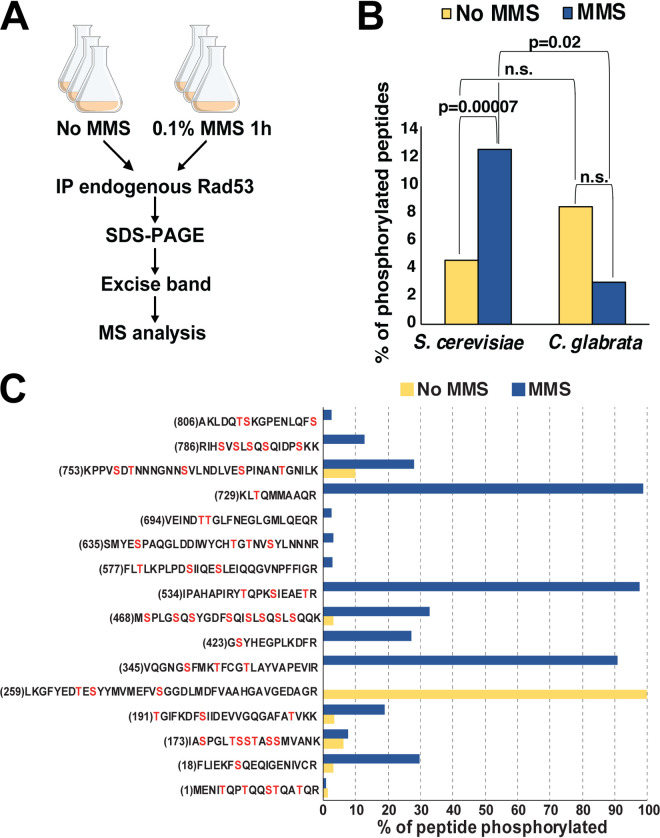
FIG 2.
Mass spectrometry (MS) analysis detected extensive DNA damage-induced Rad53 phosphorylation in S. cerevisiae but not C. glabrata. (A) Outline of the experiment. IP, immunoprecipitate. (B) The fraction of phosphorylated Rad53 peptides was significantly increased in S. cerevisiae samples, but not C. glabrata samples, derived from MMS-treated cells. The P value was calculated using the χ2 test. n.s., not significant. (C) Consistent with previous studies, our MS analysis identified extensive DNA damage-induced phosphorylation throughout ScRad53. For each peptide, the total intensity of the phosphorylated forms of that peptide was divided by the total intensity of all forms of that peptide, converted to percentages, and plotted on the y axis. The number in parentheses indicates the position of the first residue in the peptide. Serines and threonines are shown in red.