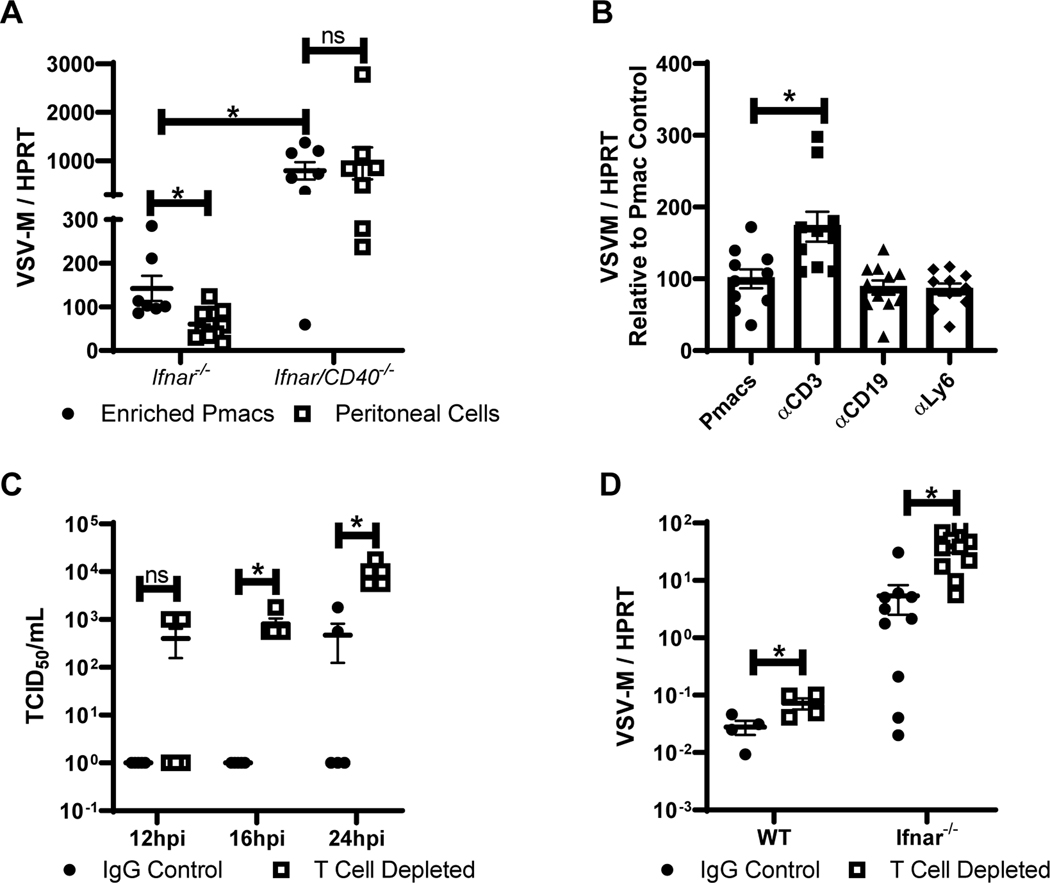
Figure 3. CD40 restriction of EBOV and rVSV/EBOV GP infection in peritoneal cells requires CD3+ T cells.
A) Peritoneal cells from male Ifnar−/− and Ifnar/CD40−/− mice were isolated. Forty-eight hours after isolation, cells were either washed to remove non-adherent cells, or incubated in the presence of non-adherent cells and infected with rVSV/EBOV GP (MOI=0.1). RNA was isolated 24 hours following infection and viral RNA was quantified by qRT-PCR. B) Peritoneal cells were isolated from male Ifnar−/− mice and cells expressing the indicated surface protein were removed via magnetic bead separation. The remaining cells were infected with rVSV/EBOV GP (MOI=0.1). RNA was isolated at 24 hours and quantified by qRT-PCR. C-D) Female C57BL/6 Ifnar−/− mice were injected i.p. with antibodies against CD4 and CD8 (200 μg each) or appropriate IgG controls. Twenty-four hours later, mice were infected i.p. with a sublethal dose of rVSV/EBOV GP. At 24 hours, serum was collected and titers were quantified by endpoint dilution on Vero cells (C) or peritoneal cell RNA was harvested, and viral RNA was quantified by qRT-PCR (D). All experiments were performed three times. All qRT-PCR is quantified by delta Ct method comparing VSV-M gene to HPRT. * indicates p<0.05.