Figure 4.
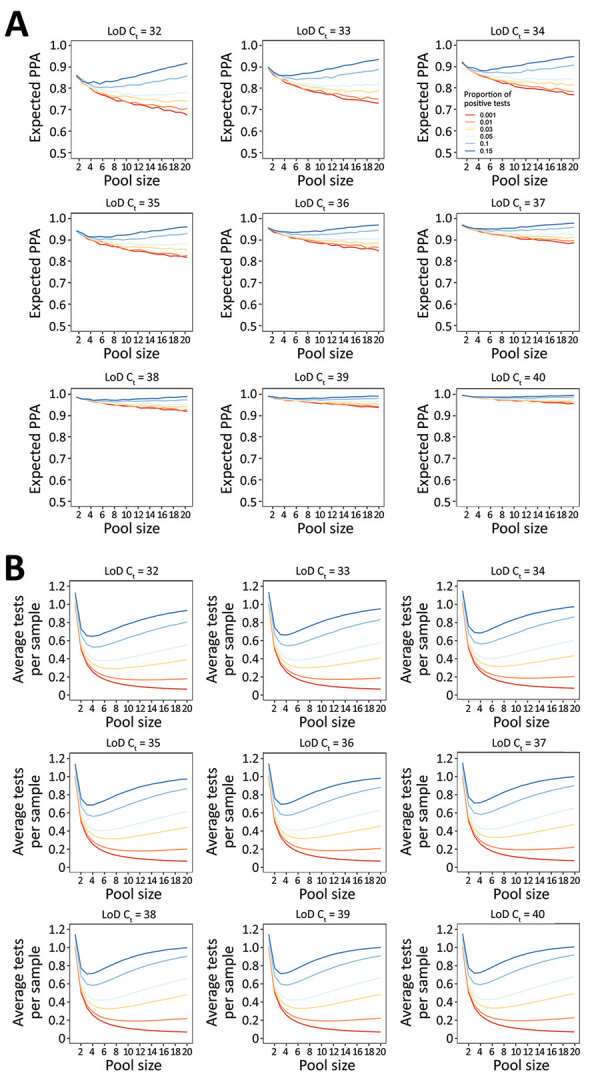
Performance of nucleic acid amplification tests for detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in prospectively pooled specimens. Model-estimated PPA and testing efficiency, by pool size, proportion of tests positive, and assay analytical sensitivity as approximated by the Ct corresponding to the 95% LoD. For these estimates, the population viral load distribution has been held constant at 15% of samples with Ct values >35. A) Expected PPA between pooled and individual testing at pool sizes of 1–20. PPA decreases with decreasing proportion of tests positive (indicated by colored lines in each plot) and increases with increased analytical sensitivity (each panel). This result occurs because the proportion of individual samples with a Ct value above each LoD decreases as the Ct LoD increases. B) Estimated average tests per sample that would be performed at each pool size, with a lower number of average tests per sample corresponding to higher testing efficiency. Efficiency increases with decreasing proportion of test results positive, and slightly decreases with increased analytical sensitivity because more pools detected results in an increased number of individual tests performed at the deconvolution step. Ct, cycle threshold; LoD, limit of detection; PPA, positive percent agreement.
