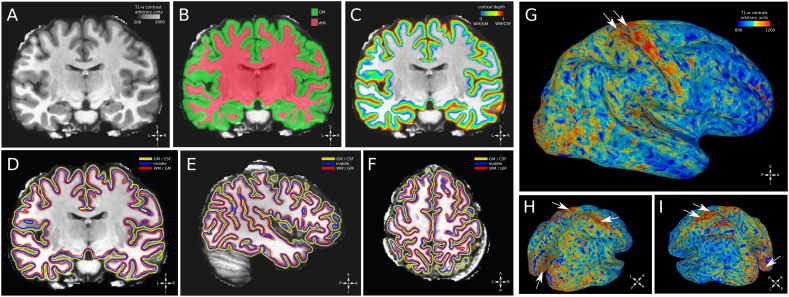
Fig. 1.
Processing and segmentation. A: T1-w contrast, coronal slice from a single participant, skull removed. B: white matter and grey matter segmentation results, superimposed to a coronal slice, T1-w contrast, single participant. C: equi-volume cortical depth map superimposed to a coronal slice, T1-w contrast. D: white matter/grey matter surface, middle surface and grey matter/cerebro-spinal fluid surface superimposed to a coronal slice, T1-w contrast. E: same as panel D, surfaces superimposed to a sagittal slice, T1-w contrast. F: same as panel D, surfaces superimposed to a horizontal slice, T1-w contrast. G: whole brain surface reconstruction (middle surface), T1-w contrast is mapped over the surface using linear interpolation from a single participant. White arrows indicate motor cortex and somatosensory cortex, showing remarkably high T1-w signal, indicative of the higher myelination of this location compared to neighbouring location (Glasser and Van Essen, 2011, Sereno et al., 2012, Fracasso et al., 2016). H: same as panel G, angled view shows high T1-w signal at the level or the calcarine fissure (white arrows in the posterior part of the brain). White arrows in the superior part of the brain indicate motor cortex and somatosensory cortex. I: same as H, rotated view.