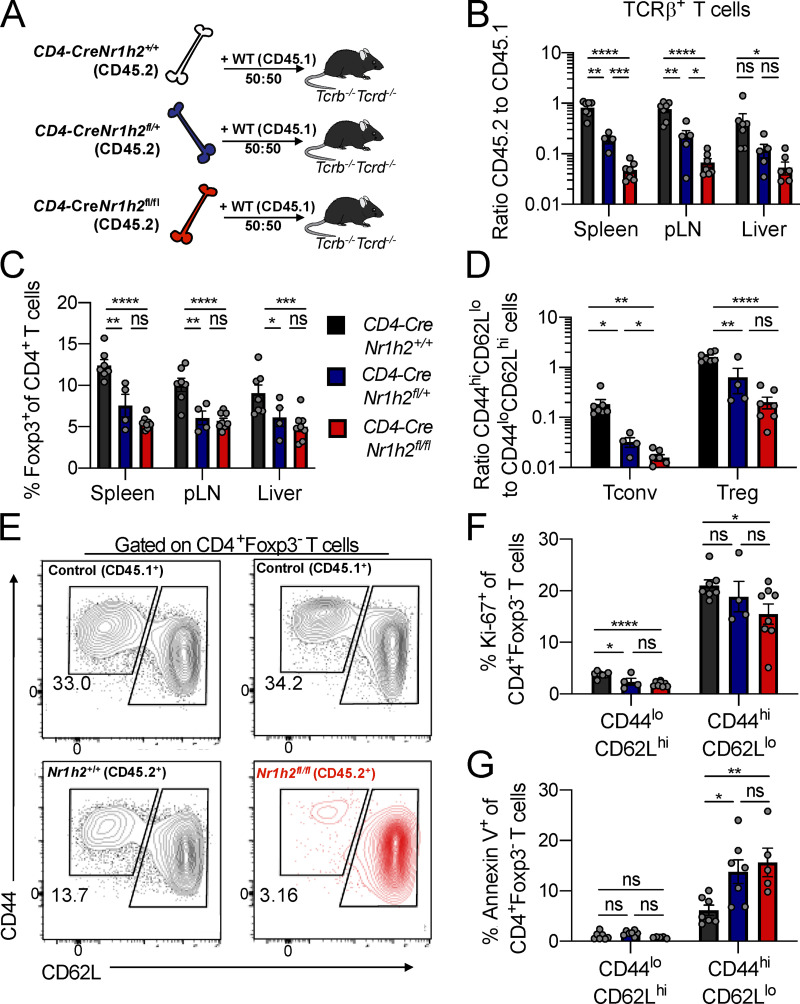
Figure 2.
LXRβ-deficient T cells are competitively unfit. (A–G) CD45.2+ BM precursor cells from CD4-CreNr1h2+/+, CD4-CreNr1h2fl/+, or CD4-CreNr1h2fl/fl animals were mixed at a 1:1 ratio with CD45.1+ calibrator cells from WT donors and transferred into lethally irradiated mice. Recipients were analyzed 8 wk after reconstitution. (A) Experimental design of mixed BM chimera experiments. (B) Ratio of CD45.2+ to CD45.1+ T cell numbers in indicated tissues. (C) Percentages of Foxp3+ T reg cells as a fraction of CD4+ T cells within the CD45.2+ compartment at the indicated organs. (D) Ratio of effector (CD44hiCD62Llo) to resting (CD44loCD62Lhi) T reg (CD4+Foxp3+) and conventional (CD4+Foxp3−) T cell numbers in the spleen. (E) Representative flow cytometry plots showing the activation status of recipient-matched CD45.2+ (CD4-CreNr1h2+/+ or CD4-CreNr1h2fl/fl) and CD45.1+ (WT control) T cells. (F and G) Quantification of Ki-67+ (F) and Annexin V+ (G) conventional CD4+T cells in the spleen. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 4–7). ns, nonsignificant = P > 0.05; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA followed by the Holm-Šídák correction. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.