Figure 6.
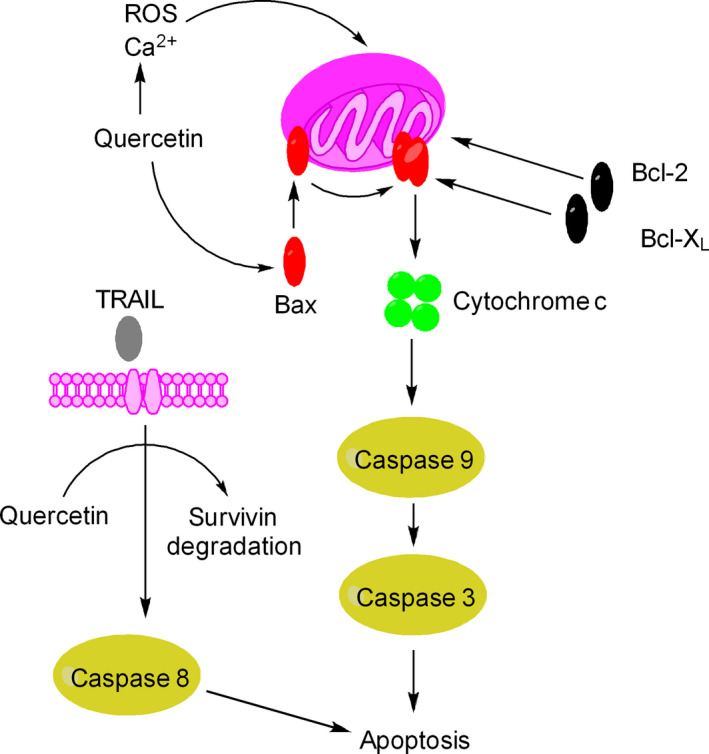
Molecular mechanism of quercetin‐induced apoptosis. Quercetin is a strong proapoptotic agent and activates both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis. Quercetin elevates the intracellular levels of ROS and Ca2+ leading to depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential, release of cytochrome c and activation of caspases such as caspase 9 and caspase 3. Alternatively, quercetin promotes translocation of Bax from cytosol into mitochondria membrane leading to depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential and subsequently induction of apoptosis. Penetration of Bax into mitochondrial membrane is normally inhibited by Bcl‐2 and Bcl‐XL proteins. Quercetin can promote TRAIL‐induced apoptosis by stimulating degradation of survivin and activation of caspase 8.
