Figure 1. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing (scRNA-Seq) Reveals Cellular Heterogeneity in Neonatal Hearts.
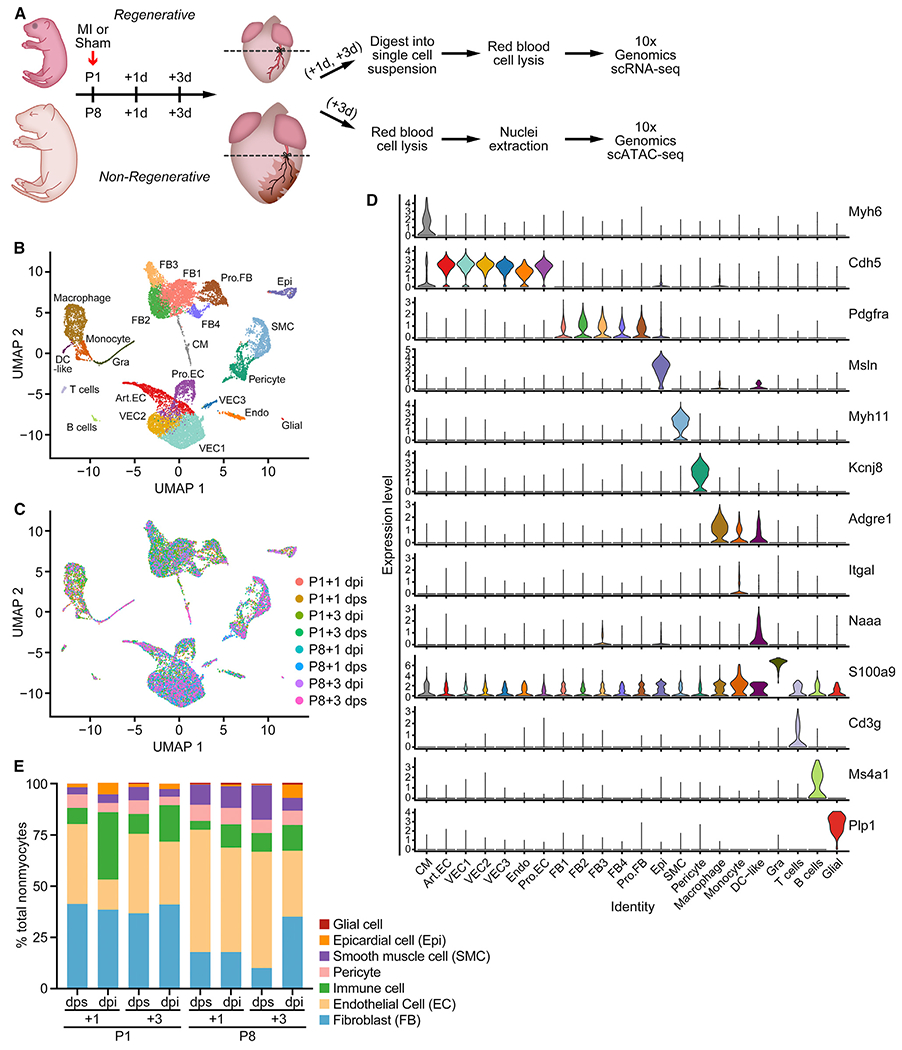
(A) Schematic of experimental design for the single-cell analyses. MI or sham surgeries were performed on P1 and P8 hearts. Ventricles below the ligation plane (indicated by the dashed lines) were collected at 1 or 3 days post-surgery for scRNA-seq, and 3-day post-surgery samples were collected for scATAC-seq. n = 8–12 animals were used for tissue collection. n = 1 sequencing library was generated for each time point and condition.
(B and C) UMAP plots showing single-cell transcriptomes analyzed in the study, color coded for cell clusters (B) or sample origin (C). For each time point, one scRNA-seq library was generated using pooled tissues dissected from 8–12 individual animals to control the differences among individual animals and dissection variations.
(D) Stacked violin plots showing expression of marker genes for each cluster. Cell clusters are color coded according to the UMAP plot in (B).
(E) Percentage of each cell type over all nonmyocytes in each scRNA-seq sample. Endothelial cells (ECs) contain Art.EC, VEC1, VEC2, VEC3, Pro.EC, and Endo clusters. Fibroblasts (FBs) contain FB1, FB2, FB3, FB4, and Pro.FB clusters. Immune cells contain macrophage, DC-like, monocyte, and Gra clusters. Art.EC, arterial endothelial cell; CM, cardiomyocyte; dpi, days postinjury; dps, days post sham; Endo, endocardial cell; Epi, epicardial cell; Gra, granulocyte; Pro.EC, proliferating endothelial cells; Pro.FB, proliferating FB; SMC, smooth muscle cell; VEC, vascular endothelial cell. See also Figure S1 and Tables S1 and S2.
