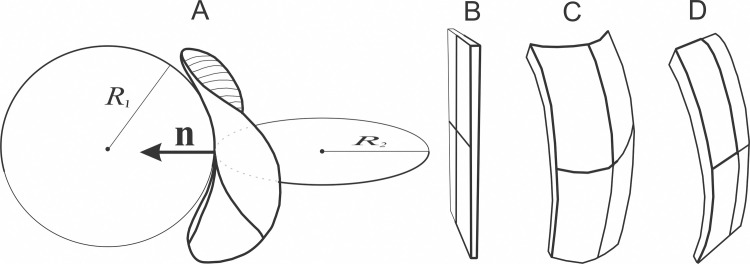
Fig 2. An area element of the membrane with the normal (indicated by a vector n) and the principal directions.
The radii of the circles that fit the shape of the normal cuts in the principal directions at the chosen point are shown and the radii R1 and R2 determining the local principal curvatures C1 = 1/R1 and C2 = 1/R2, are indicated. Possible local shapes of a membrane favoring A: Saddle–like (H ≠ D ≠ 0), B: Flat (H = D = 0), C: Globular (H > 0, D ≃ 0 or H < 0, D ≃ 0) and D: Cylindrical (H = ∓D ≠ 0) shape.