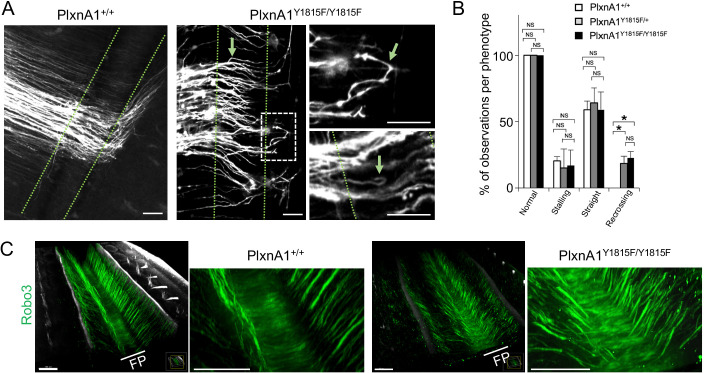
Figure 1. Y1815F mutation in PlxnA1 induces commissural axon recrossing and disorganized trajectories.
(A) Microphotographs illustrating commissural tracts of PlxnA1+/+ and PlxnA1Y1815F/Y1815F E12.5 open-books labeled with DiI. In PlxnA1+/+ embryos, axons extend straight toward the floor plate (FP), cross the FP, and turn rostrally at the FP exit. In PlxnA1Y1815F/Y1815F embryos, some axons turn back or are misdirected during the navigation of the FP (indicated by green arrows). The FP is delimited by dashed green lines. (B) Quantitative analysis of commissural axon phenotypes (PlxnA1+/+, N = 3 embryos; PlxnA1+/Y1815F, N = 5 embryos; PlxnA1Y1815F/Y1815F, N = 4 embryos). Data are shown as the mean ± s.e.m., Student's t-test has been applied, *: p<0.05. (C) Light sheet imaging of the spinal commissural tracts in PlxnA1+/+ and PlxnA1Y1815F/Y1815F embryos at E12.5, immunostained with anti-Robo3 antibody. Scale bar: 50 μm in (A), 150 μm in (C).