Fig 5. Molecular mechanism for nucleotide translocation through the HIV-1 CA hexamer.
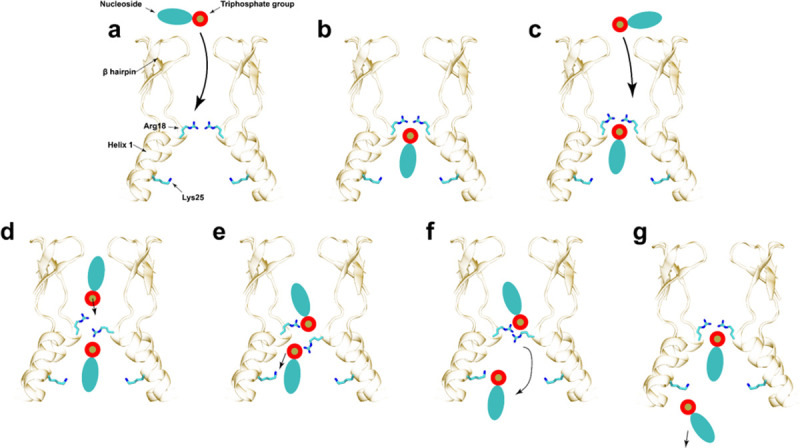
(a) A nucleotide diffuses freely between the exterior (top) of the capsid and the central cavity. (b) Subsequently, the nucleotide binds to Arg18 and Lys25 in a canonical binding conformation. Exact interactions between the nucleoside and helix-1 confer nucleotide-type specificity. (c) A second nucleotide freely diffuses between the exterior and the central cavity of CA. (d) The phosphate group of the second nucleotide interacts with Arg18 delocalizing the interactions between the first nucleotide and the Arg18 ring. (e) The second nucleotide enhances interactions between Lys25 and the first nucleotide. (f) Interactions between Lys25 and the phosphate group are weak and thermal fluctuations facilitate dissociation of the dNTP into the interior of the capsid. (g) The second nucleotide now occupies the canonical binding position (b) for a single nucleotide in the cavity.
