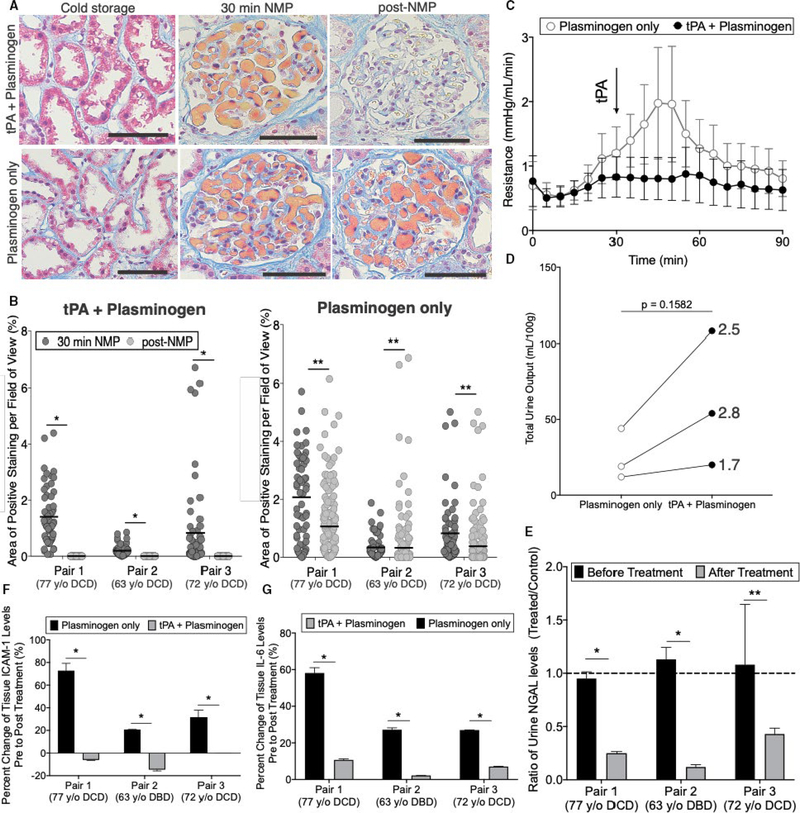
FIGURE 4.
Paired donor organs suggest tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) + plasminogen treatment improves organ viability. A, Representative images and B, quantification of area of microvascular obstruction are shown for paired kidneys from the same donor treated with tPA + plasminogen or plasminogen only (*P < .0001, **P < .05; Mann-Whitney t test). Scale bars represent 100 μm. C, Resistance time traces as measured during normothermic machine perfusion (NMP) for plasminogen only vs tPA + plasminogen. Data points represent the mean and error bars signify standard error of the mean for each group of 3 kidneys. Arrow denotes point of tPA administration. D, Total urine output normalized to the mass of each kidney as measured after 90 min of NMP (*P = .1582; paired t test); lines connect paired organs from the same donor. E, Urine NGAL ratios of tPA + plasminogen relative to plasminogen only controls before and after treatment (*P < .00001, **P = .0188; multiple t tests). F, Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1; *P < .001; multiple t tests) and G, interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels as measured by ELISA on tissue lysates (*P < .00001; multiple t tests). Samples were processed in triplicate