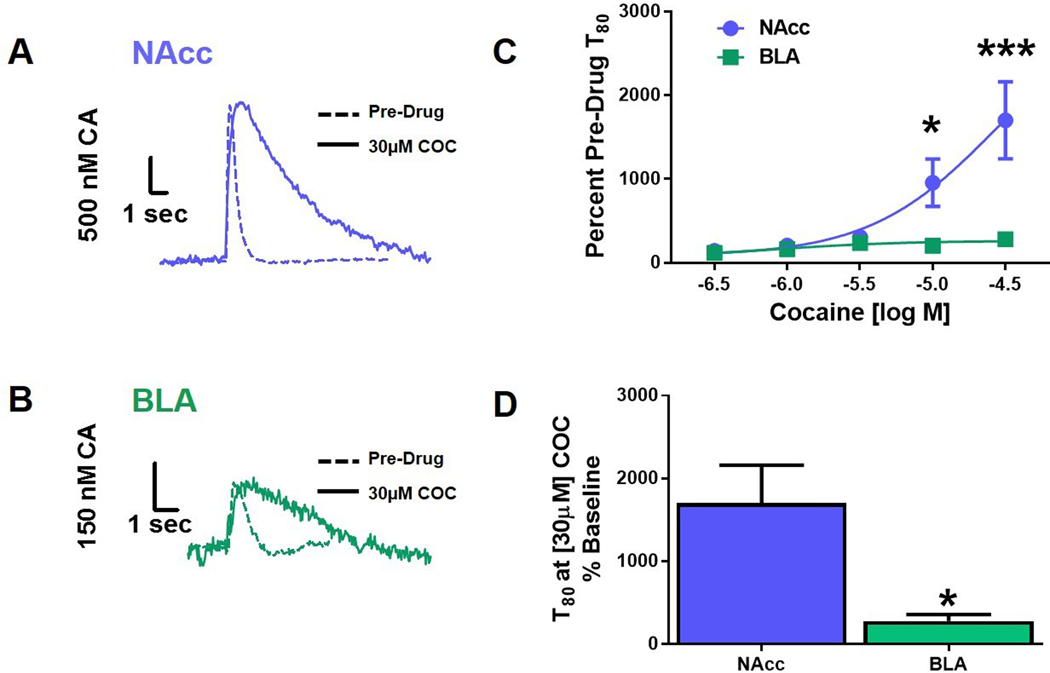
Figure 6: Inhibition of catecholamine uptake by cocaine is greater in the NAcc compared to the BLA.
(A) Representative traces of evoked catecholamine release and uptake in brain slices containing the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) at baseline (Pre-Drug) and 30μM cocaine (COC), overlaid. (B) Represented traces from basolateral amygdala (BLA)-containing brain slices at baseline and 30μM COC overlaid. (C) Cocaine (10μM and 30μM) significantly impaired catecholamine clearance in the NAcc compared to the BLA, (p<0.05, and p<0.001, respectively). (D) An increase in NAcc T80 revealed a significantly greater potency of COC in the NAcc, compared to the BLA (p<0.05). NAcc = nucleus accumbens core; BLA = basolateral amygdala; CA = catecholamine; COC = cocaine; *p<0.05; ***p<0.001. N=5 animals/group