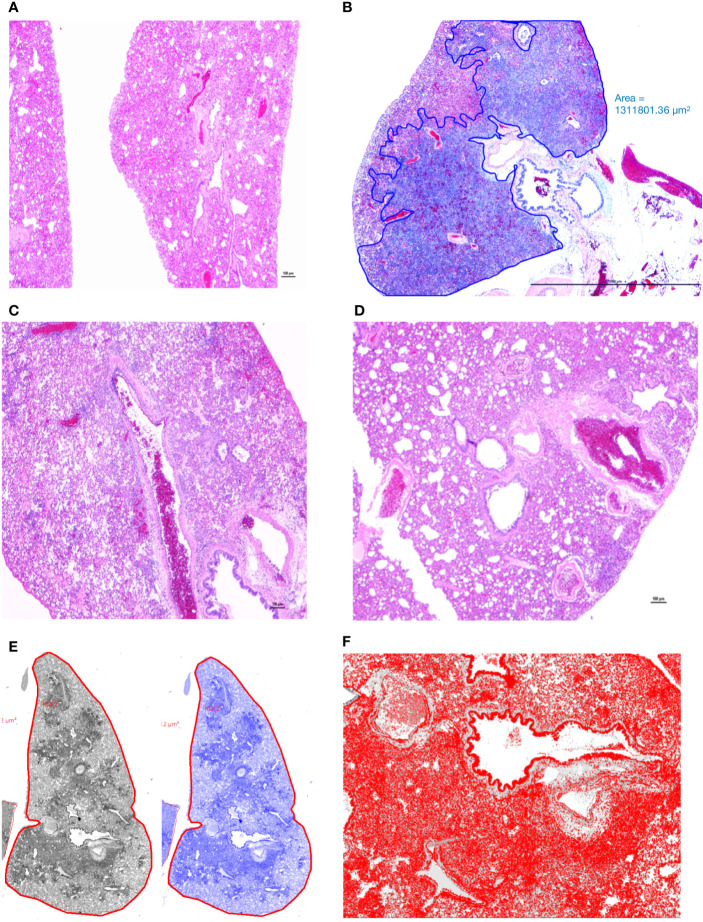
Figure 3.
Manual annotation and comparison of histological scores of bronchointerstitial pneumonia in control and treated hamsters. (A) Lungs from an uninfected hamster were visualized and scored for lack of significant hypercellularity. (B) Affected parenchyma of infected hamsters (Untreated) characterized by intense hypercellularity is manually annotated (blue) excluding unaffected lung parenchyma, main stem bronchi and hilar adipose tissue. (C) Lung section from a control antibody treated hamster (Ab Control) is showing marked reduction in total cellularity or inflammation. (D) Lung section from a low-dose AvGn-B antibody-treated hamster (AvGn-B Low) showing very significant reduction of inflammation reducing the total area of affected pulmonary parenchyma. (E) After manual annotation depicted in (B) and based on the generated montage including training set and threshold, the automated classifier to discriminate lesional from non-lesional parenchyma was generated in grey and then in blue. (F) After manual annotation of affected lungs, all of the defined classes in preset ROI, i.e., inflammatory foci characterized by infiltration of inflammatory cells into alveolar spaces were identified to generate total number of nuclei (hematoxylin and DAPI-stained nuclei) that were accurately recorded.