Fig. 1.
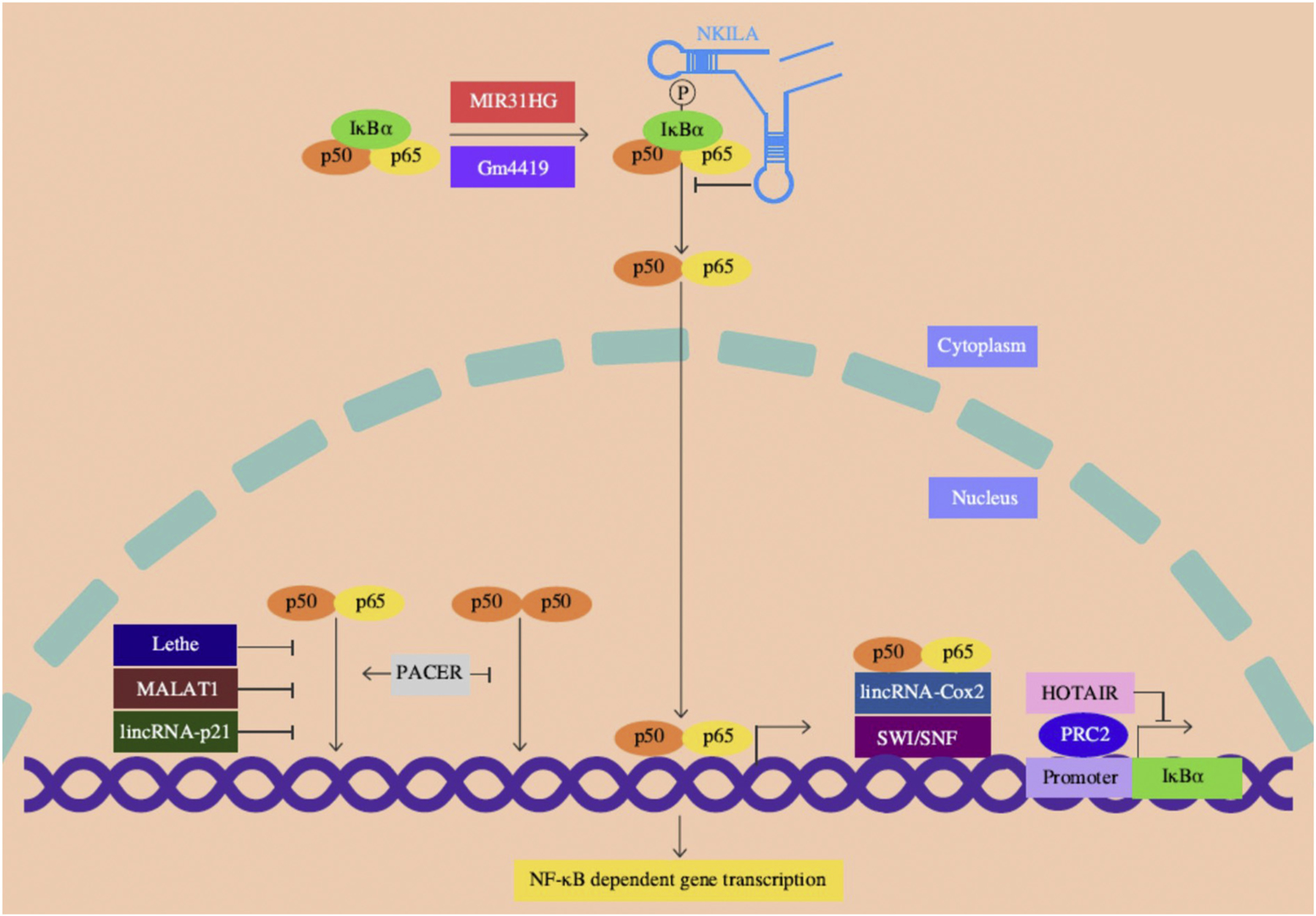
Schematic representation for the role of lncRNAs in NF-κB signaling. NKILA associate with the NF-κB-IκB complex in the cytoplasm masking the IκB phosphorylation thereby suppressing its degradation and NF-κB activation. Lethe, MALAT1 and lincRNA-p21 are largely located in the nucleus, directly associate with p65 and prevent the p65/p50 heterodimer binding to the target promoters. Upon LPS stimulation, PACER occludes the binding of inhibitory p50/p50 homodimers but promotes the active p65/p50 heterodimer formation at the COX2 promoter. HOTAIR acts in trans of the IκBα gene and suppresses its expression partly by recruiting PRC2, which is a chromatin-modifying enzyme complex. The lincRNA-Cox2 facilitate the p65/p50 heterodimer binding to the target site by recruiting the SWI/SNF complex. Under normal conditions, MIR31HG is located in the nucleus. Upon inflammatory stimulation, MIR31HG is exported to the cytoplasm, induces IκBα phosphorylation by direct interaction leading to NF-κB activation. Gm4419 can also physically associate with and induce IκBα phosphorylation and NF-κB activation. Other lncRNAs discussed in the text are not indicated as their mechanistic association with NF-κB signaling is not clearly known. Abbreviations: HOTAIR: HOX transcript antisense RNA; IκBα: inhibitor of kappa B alpha; lincRNA-p21: long intergenic noncoding RNA-p21; MALAT1: metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; MIR31HG: MIR31 host gene; NKILA: NF-κB interacting lncRNA; PACER: P50 associated cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) extragenic RNA; PRC2: polycomb repressive complex 2; SWI/SNF: switch/sucrose nonfermentable.
