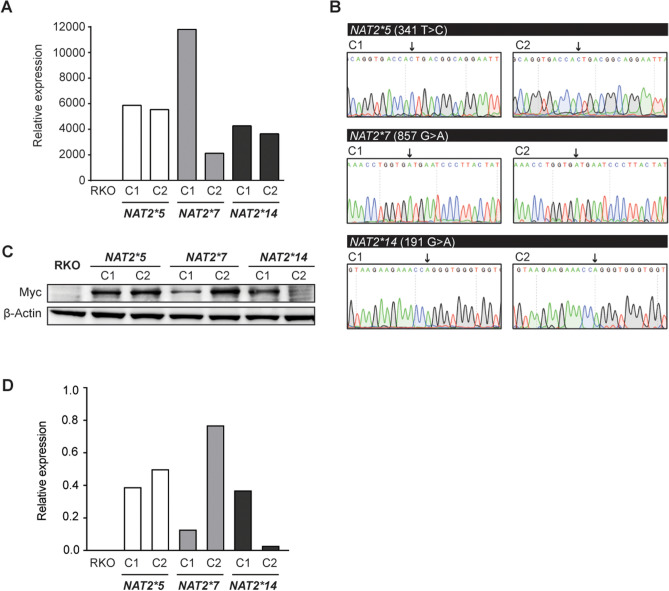
Figure 3.
Generation of stable CRC cell clones expressing NAT2 slow acetylator variants. (A) Two clones encoding each of the indicated NAT2 slow acetylator variants were chosen for downstream analyses based on their expression of NAT2 RNA relative to parental RKO cells. Data from one representative experiment shown. (B) Sanger sequencing revealed the correct 341 T > C, 857 G > A, and 191G > A substitutions in the NAT2 coding region (black arrows) to generate the NAT2*5, *7 and *14 alleles. (C) Protein expression of NAT2 slow acetylator variants by immunoblotting. A Myc-tag antibody was used to detect recombinant NAT2 with β-actin as loading control. Full-length immunoblots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 4. (D) Quantification of immunoblots shown in (C). Protein expression levels were normalized against β-actin.