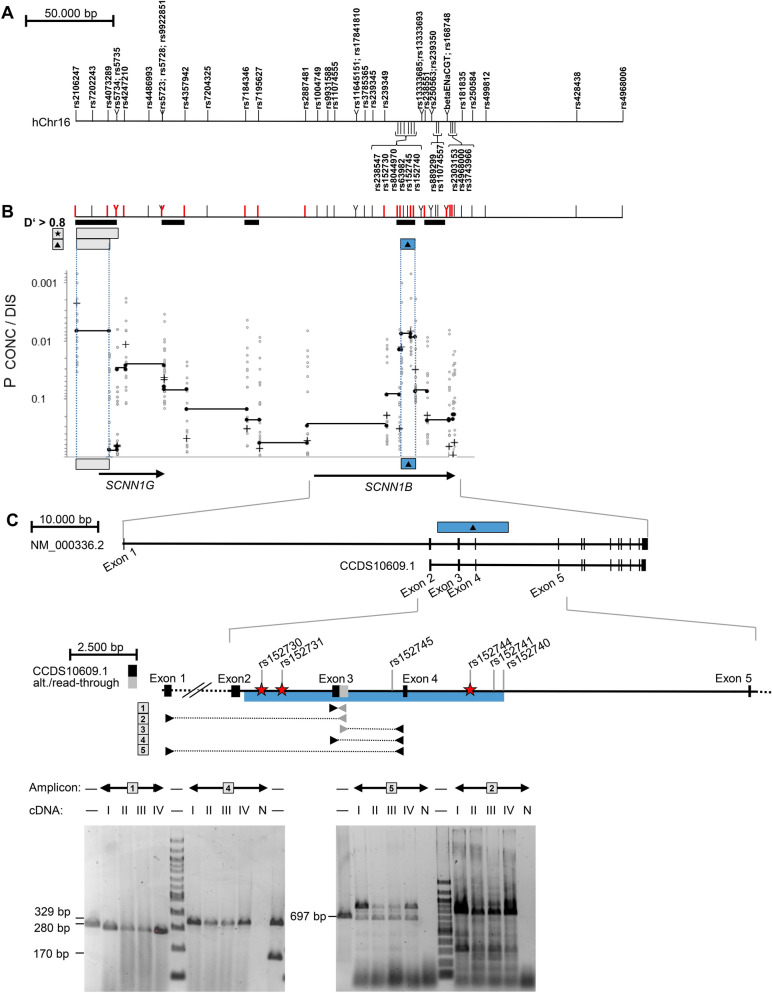
Figure 1.
Mapping of the association signal determining intrapair discordance among F508del-CFTR homozygous CF sibling pairs, identification of an alternative SCNN1B transcript and position of SNPs analyzed by EMSA-PSeq. (A) Position of SNP and microsatellite markers on the genomic sequence of the SCNN1G/SCNN1B region. The position of genetic markers was derived from the genomic sequence on NC_000016 (assembly 03-Feb-2014; GRCh38; region 23302270–23381299). Nomenclature of SCNN1B exons was derived from Voilley et al. 199559 and Saxena et al. 199860, who have described exon/intron borders and the coding sequence for a 640 amino acid SCNN1B protein encoded by 13 exons (NP_000327.2; GI: 124301196; CCDS10609.1). The position of intragenic primers and expected sizes of amplicons covering exon 1–5 of SCNN1B are based on this coding sequence. SNPs rs5735, rs5723, rs1004749, rs238547, rs152730, rs250536 and on microsatellite betaENaCGT were previously typed11 and further 49 SNPs were genotyped for fine-mapping (this work). (B) Haplotype blocks, informative markers and association signals in the SCNN1B/SCNN1G region. Markers depicted in red are informative (minimal allele frequency > 0.4) and were used to describe haplotype blocks (a measure of linkage disequilibrium D′ > 0.8) and map association signals as previously described13. Briefly, to map association signals, we defined genomic segments by adjacent ancestral informative markers that isolate the fragment that carries the causative variant(s)13. p values were generated by the software package FAMHAP55–57. p values refer to the best signal observed for a two-marker-combination of the 20-marker-set (Pbest) and the corrected value for multiple testing of 20 markers (Pcorr). Symbols refer to: Star: signal obtained by transmission disequilibrium test in the set of 37 sibling pairs families with extreme phenotypes (Pbest = 0.00101 for rs2106247–rs4073289; Pcorr = 0.0561 corrected for multiple testing of 20 informative markers); Filled triangle: association with intrapair discordance (Pbest = 0.0007 for rs2106247–rs152745; Pcorr = 0.0397 corrected for multiple testing of 20 informative markers) comparing 14 discordant and 23 concordant patient pairs. Uncorrected raw p values are shown for single markers (+), 2-marker-haplotypes of adjacent informative markers (filled circles; genomic segments spanned by two adjacent markers are linked by a black line) and 2-marker-haplotypes of non-adjacent markers (open circles). The SCNN1B association signal observed for intrapair discordance (filled triangle) was seen on the neighboring segments rs152730–rs152745 (Praw = 0.0075) and rs152745–rs152740 (Praw = 0.00869). A second independent association signal with intrapair discordance in the SCNN1G locus colocalizes with the previously noted survivor effect at SCNN1G11 and was excluded from further analysis because of this confounding factor. (C) SNPs targeted by EMSA-PSeq and combinatorial PCR describing an alternative transcript generated by exon-read-through. Interaction partners of SNPs rs152730, rs152731 and rs152744, indicated by red star symbols, have been characterized by EMSA-PSeq. Equivalent amounts of cDNA from T84 (I), 16HBE14o-(II), CFTE29o-(III) and CFBE41o-(IV) or no template (negative control, N) were analyzed by combinatorial PCR with 5 amplicons. The grey intronic sequence (amplicon 1, 2, 3) was derived from ESTs BM694355 and BU730506 (see text and supplement for details). Intron-spanning primers targeting the SCNN1B reference mRNA (amplicons 4 and 5) as well as amplicon 1 targeting the alternative transcript and the 5′ UTR were observed in all cell lines. The size of amplified products from all amplicons was in accordance with the expected length. Size markers are loaded in lanes indicated by “—” and contain either a 100-bp-ladder or PCR products of 697 bp, 329 bp, 280 bp and 170 bp as indicated adjacent to the gel. Sanger sequencing of amplicon 1 confirmed the exon3-read-through and Sanger sequencing of amplicon 2 products verified its identity derived from a spliced mRNA as it showed a joined exon1 and exon2 sequence.