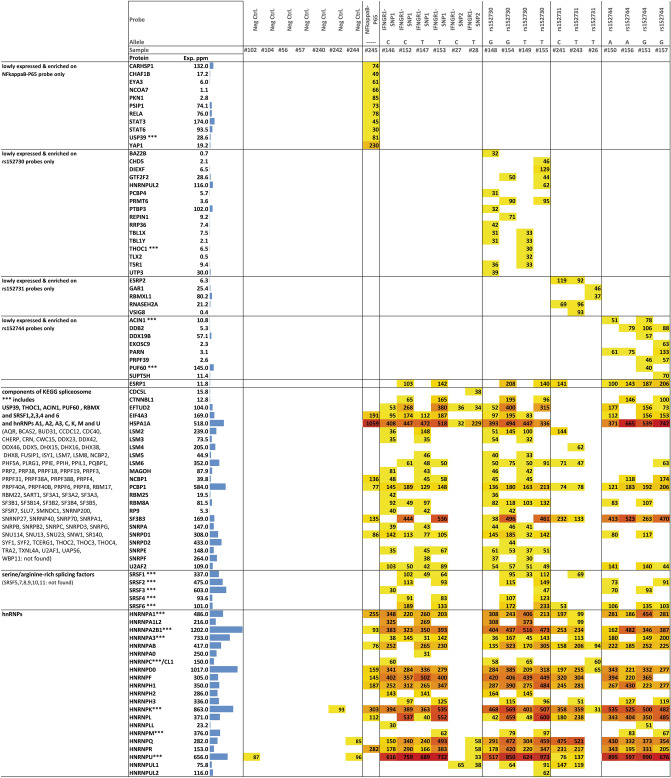
Figure 4.
Proteins specific for rs152730, rs152731 and 152744 and abundantly present components of the spliceosome identified by EMSA-PSeq. Numbers correspond to MASCOT scores obtained for protein sequencing (primary data provided in: raw data xls supplement R3) which is a probability score that describes – 10LOG10(P), with P being the probability that the detected protein represents a significant match in this data set. ESRP2 was captured on rs152731 probes with a MASCOT score of 119 (C-allele, p = 10–12) and 92 (T-allele, p = 10–9), respectively. Data is shown for proteins specific for one SNP (top 40 rows), proteins that exhibit partial specificity (spliceosomal proteins) and proteins that were unspecifically found in the majority of probe-derived samples but were absent from the majority of negative controls (hnRNPs). Proteins specific for one probe or one SNP which were identified from the dataset derived for 25 EMSA-PSeq samples based on 1. Their absence from empty negative control samples 2. Their absence from EMSA-PSeq samples obtained with probes for other analyzed SNPs 3. Their expression levels of less than 200 ppm according to pax-db and 4. Their annotated capabilities to interact with nucleic acids (see SupplFig 3 for details). Data on ESRP1 is provided for comparison as both, ESRP1 and ESRP2 were interrogated in an association study (see Fig. 5). As many RNA-binding proteins were found among the proteins identified as SNP-specific, and as an alternative SCNN1B transcript has been observed, EMSA-PSeq data was systematically screened for constituents of the spliceosome. Exp. ppm denotes expression values retrieved from the Protein Abundances Across Organisms-database pax-db61 for the data set “colon integrated”, except for EYA3, BAZ2B, DIEXF, PRMT6, TLX2, UTP3, LSM3, LSM5, RP9 [Whole organism, (PeptideAtlas, Aug 2014)] and TLX2 [Whole organism (Integrated)]. Samples #26, #27 and #28 have been derived from denaturing SDS-polyacrylamide gels, hence these lack the multiprotein complexes observed in all other samples derived from native polyacrylamide electrophoresis. Details on experimental conditions are described in SupplTab 9.