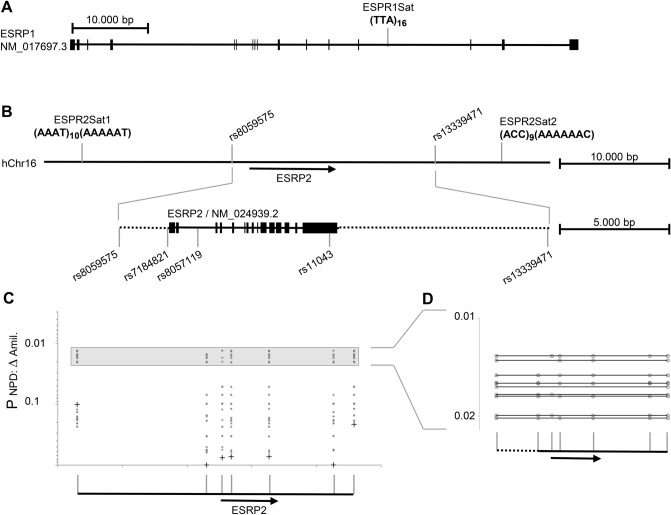
Figure 5.
Association study on ESRP1 and ESRP2. (A) Position of intragenic microsatellite marker ESRP1Sat within ESRP1. ESRP1 was selected as control as this protein was identified at most probes used for EMSA-PSeq. In other words, no enrichment of ESRP1 with any probe used for EMSA-PSeq has been observed. No association of the ESRP1Sat allele distribution with CF disease severity or manifestation of the basic defect was seen (Praw > 0.2; data not shown). (B) Five SNPs and two intergenic microsatellite markers were typed on ESRP2. Markers on the ESRP2 locus were in strong linkage disequilibrium recognized by D′ values of 0.884, 0.918, 0.884 and 0.977 on the four segments between two adjacent SNP markers spanning ESRP2. (C,D) Analyzing markers in ESRP2, two association signals were observed: intrapair comparison of mildly versus severely affected sibling of discordant pairs was skewed (Praw = 0.1092 for ESRPSat2; Praw = 0.104 for the combination of ESRP2Sat1 and rs8057119; Pcorr = 0.323 corrected for multiple testing of 7 markers, data not shown) and an allelic association with the response to superfusion of the nasal epithelium with amiloride assessed by nasal potential difference measurement was seen (Pbest; raw = 0.0131; Pcorr = 0.068 corrected for multiple testing of 7 markers, data shown in (C,D). For this case-reference association study, F508del homozygotes with contrasting responses upon superfusion of the nasal epithelium with amiloride were compared in their ESRP2 genetic background. Cases were 16 patients with an amiloride response of 31 mV, references were 15 patients with 21 mV or less17. Raw p values of single markers are shown as “+” in (C), for raw p values obtained for multimarker haplotypes, marker positions are shown as “◯” in (C,D). For 0.02 > Praw > 0.01, multimarker combinations are displayed in (D).