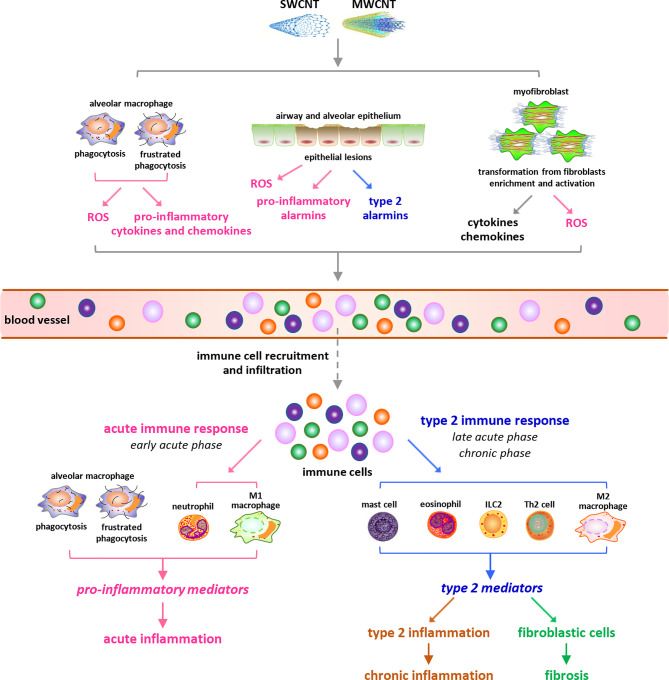
Figure 1.
Overview of carbon nanotube (CNT)-induced lung inflammation. Under exposure to CNTs, various immune cells are recruited from blood vessels and infiltrate into lung tissues, triggered by cytokines, chemokines, ROS, and alarmins that are induced by CNTs through distinct mechanisms. During the early acute phase response, neutrophils and M1 macrophages are dominant and active to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors, resulting in acute inflammation. Whereas during the late acute phase response, the immune cells implicated in type 2 immune response are dominant and produce type 2 cytokines and mediators, leading to type 2 inflammation. The activation of type 2 immune response mediates the transition from acute inflammation to chronic inflammation and promotes the development of lung fibrosis.