Fig. 2.
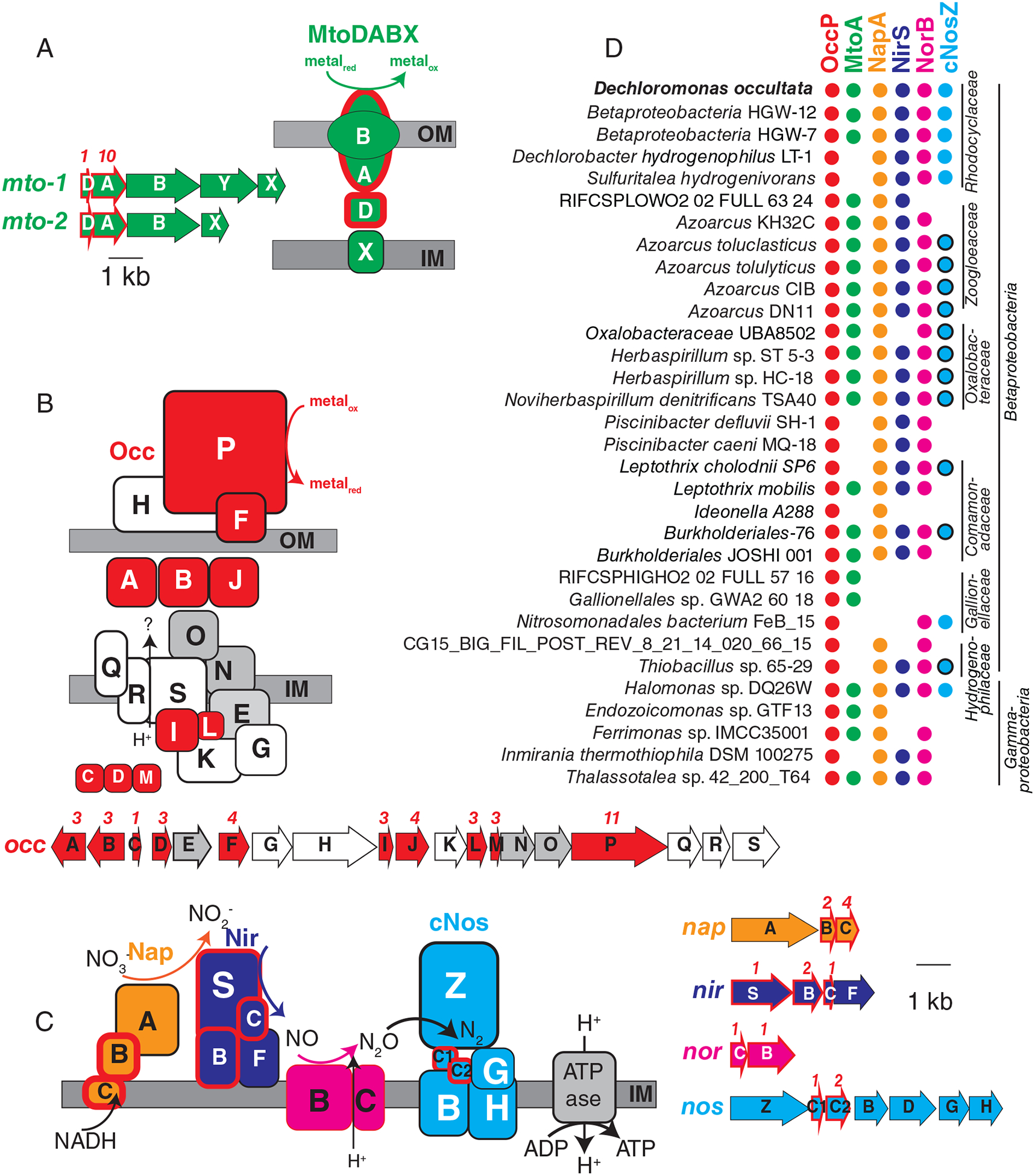
Gene arrangement, predicted protein location and taxonomic distribution of major expressed respiratory complexes in ‘Ca. D. occultata’. A: MtoDAB(Y)X porin-cytochrome c electron conduit; B: OccA-S; C: denitrification complexes (Nap, Nir, Nor and cNos); D: Occurrence of key marker genes in Betaproteobacteria and Gammaproteobacteria with >95% complete genomes that encode OccP. Protein sequences from ‘Ca. D. occultata’ were used as a query against a genome database and searched using PSI BLAST. Matches with identities >40%, query coverage >80% and E values <10−5 were considered positive. Red fill around genes and proteins indicate cytochrome-c proteins. Black outlines around blue circles in D indicate type I nitrous oxide reductase to distinguish from blue dots (type II/cytochrome-nitrous oxide reductase). Grey-shaded genes on the occ gene cluster indicate 6-NHL repeat proteins. Protein locations shown are based on P-sort predictions. Numbers above genes indicate the number of CxxCH motifs predicted to bind cytochrome c. IM: inner membrane; OM: outer membrane. For more details, see Table 1 and Table S3.
