Fig. 2. Schematic diagrams for four major categories of marine-terminating glaciers, with cold, fresh polar water (PW) on top of warm, salty AW.
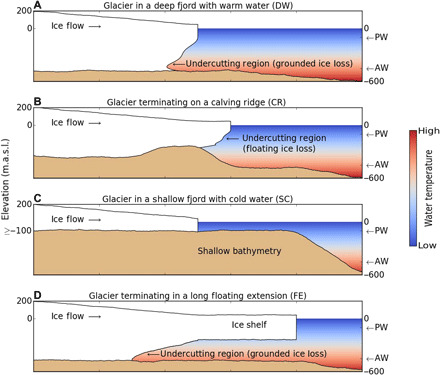
(A) Glaciers in deep fjords with warm AW (DW) that undercuts the glacier face to affect basal resistance. (B) Glaciers with temporary floating extensions on a shallow ridge (SC), for which undercutting does not affect basal resistance. (C) Glaciers standing in shallow, cold waters (SC). (D) Glaciers develop long (>10 km) floating ice extensions (FE). Note that glacier and bed elevations, expressed in meters above sea level (m.a.s.l.), are approximations provided for illustration.
