Fig. 3. Essential design principles of the ZEN hydrogels.
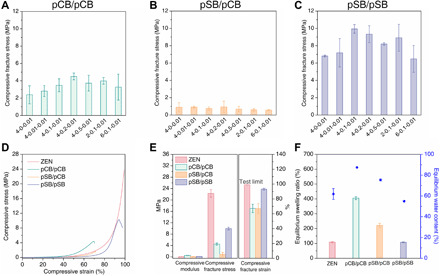
A minor component network with high swellability and a major component network with the locking effect are the essential design principles of the ZEN hydrogels. (A to C) Compressive fracture stress of pCB/pCB (A), pSB/pCB (B), and pSB/pSB hydrogels (C). The minor component network of these hydrogels was made according to the composition of 1-4-0.1. The major component network was made according to seven different compositions as indicated on the x axis. x, y, and z for x-y-z represent the molar monomer concentration, cross-linker concentration (mol % with respect to the monomer), and initiator concentration (mol % with respect to the monomer) of the corresponding network, respectively. (D to F) Representative compressive curves (D); compressive modulus, fracture stress, and fracture strain (E); and equilibrium swelling ratios and equilibrium water contents (F) of the pCB/pSB ZEN, pCB/pCB, pSB/pCB, and pSB/pSB hydrogels. The pCB/pSB ZEN and pSB/pSB hydrogels were made according to the composition of 1-4-0.1/4-0.1-0.01, while pCB/pCB and pSB/pCB hydrogels were made according to the composition of 1-4-0.1/4-0.2-0.01. Note that x, y, and z for x1-y1-z1/x2-y2-z2 represent the molar monomer concentration, cross-linker concentration (mol % with respect to the monomer), and initiator concentration (mol % with respect to the monomer) for the two component networks, respectively.
