Fig. 4 .
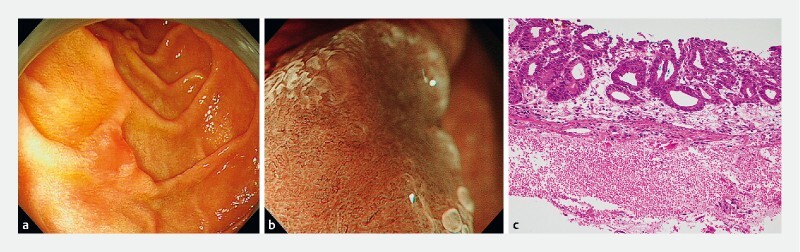
A case of duodenal adenocarcinoma without biopsy. a Endoscopic findings using conventional endoscopy with white light imaging. A reddish, slightly depressed lesion (10 mm in diameter) is seen in the second part of the duodenum. b Endoscopic findings using magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging findings (M-NBI). A clear demarcation line (DL) is visible because of differences in the vessel plus surface (VS) component between the cancerous and noncancerous mucosa. V: Proliferation of microvessels with variable sizes, asymmetrical distribution, and irregular arrangement make this an irregular microvascular (MV) pattern. S: There are areas where the marginal crypt epithelium cannot be visualized, and analysis of the white opaque substance (WOS) morphology shows it to be irregular WOS with a speckled pattern. This lesion was assessed as an irregular microsurface (MS) pattern. The VS classification of this lesion was an irregular MV pattern plus irregular MS pattern (WOS +) with a DL. Therefore, the M-NBI diagnosis was cancer. c The final histological diagnosis was a well-differentiated intramucosal adenocarcinoma.
