Figure 1.
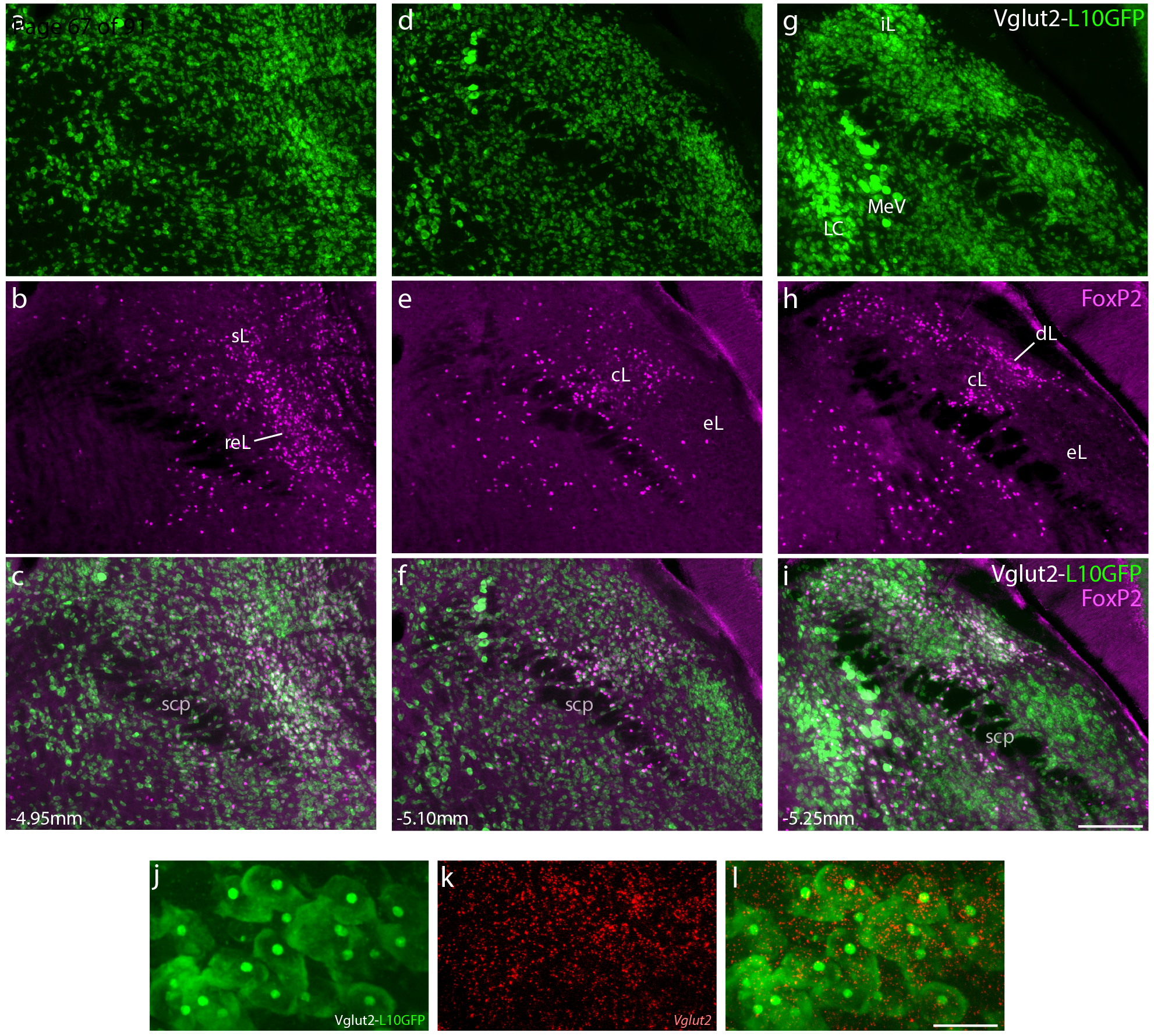
Neurons that express the transcription factor FoxP2 form a subset of the larger population of glutamatergic neurons in the parabrachial nucleus (PB). (a–i) Across three levels of the PB region, Cre-reporter expression reveals the distribution of neurons that have expressed vesicular glutamate transporter 2 (Vglut2). Approximate bregma level is shown at the bottom-left of each column. Green fluorescent protein (conjugated to the L10 ribosomal subunit; L10GFP) in Vglut2-IRES-Cre;R26-lsl-L10GFP mice represents neurons that have expressed Vglut2. Note that this includes neurons in the locus coeruleus (LC), which no longer express Vglut2 in the adult brain (Stornetta et al., 2002). Neurons with nuclear immunofluorescence labeling for FoxP2 (magenta) span the dorsal lateral (dL), central lateral (cL), rostral to external lateral (reL), and superior lateral (sL) PB subnuclei. In contrast, FoxP2 labeling is sparse in the external lateral (eL) subnucleus. Scale bar in (i) is 200 μm and applies to panels (a-i). (j-l) GFP-expressing neurons in the lateral PB neurons contain mRNA for Vglut2 (Slc17a6). Scale bar in (l) is 20 μm and applies to panels (j-k). Other abbreviations: iL, internal lateral; MeV, mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus; scp, superior cerebellar peduncle.
