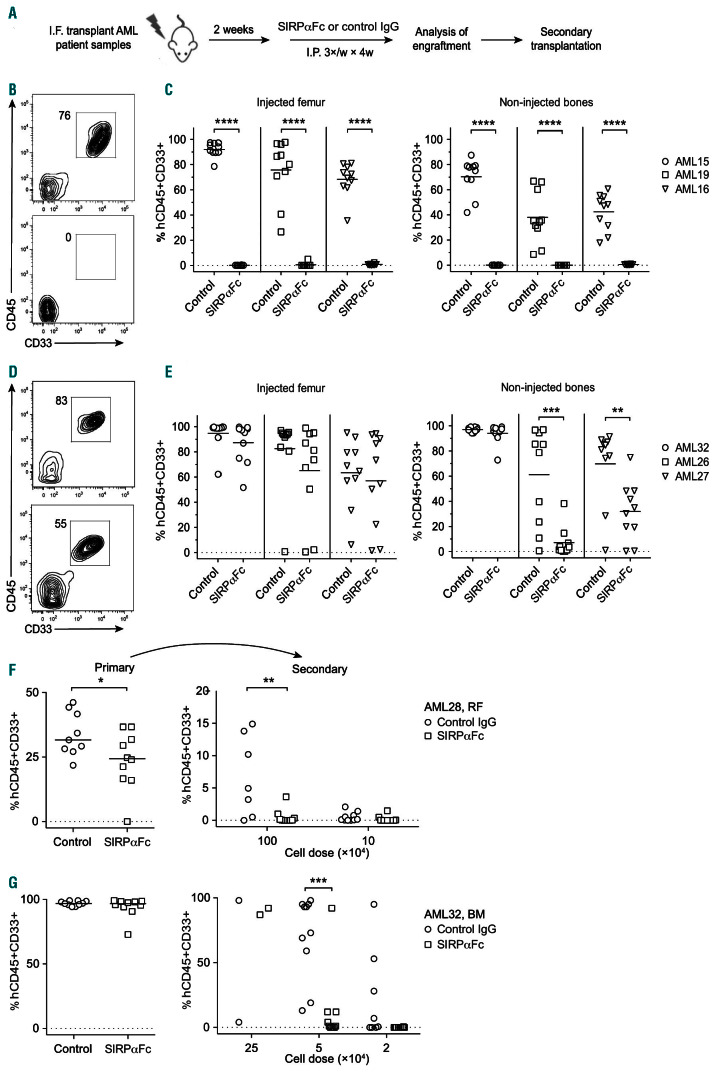
Figure 1.
SIRPαFc treatment eliminates leukemia stem cells in primary acute myeloid leukemia xenografts. (A) Schematic illustrating the experimental protocol used for in vivo drug testing. (B), (D) Representative flow cytometric analysis of human CD45+CD33+ acute myeloid leukemia (AML) engraftment in the injected femur of mice transplanted with a representative responder sample (AML19) (B) or a representative partial responder sample (AML26) (D) and treated with control IgG (top panels) or SIRPαFc (bottom panels). (C), (E) Summary of human AML engraftment in the injected femur and non-injected bones of mice treated with control IgG or SIRPαFc, as determined by flow cytometry. Three representative responder samples are shown in (C) and the non-responder (AML32) and two representative partial responder samples (AML26, AML27) are shown in (E), (F-G) Summary of human AML engraftment in the injected femurs of untreated secondary recipient mice 12 weeks after transplantation of indicated doses of AML cells pooled after harvesting from injected femurs (RF) or non-injected bone marrow (BM) of primary mice treated with control IgG or SIRPαFc, as determined by flow cytometry. A representative partial responder (AML28) is shown in (F) and the non-responder (AML32) is shown in (G). Each symbol represents one mouse. Bars indicate mean values. I.F.: intrafemoral; I.P.: intraperitoneal; *P≤ 0.05; **P≤ 0.01; ***P≤ 0.001; ****P≤ 0.0001.