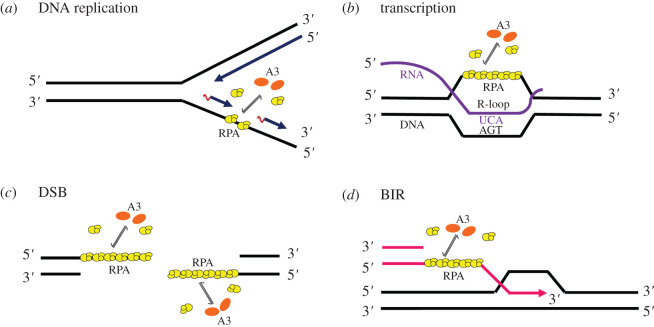
Figure 2.
A3 deamination of cellular ssDNA templates. Single-stranded substrates of A3 deamination include ssDNA intermediates generated at replication forks (a), during transcription (b), at DSBs (c) and those generated during BIR (d). RPA (yellow) is bound to ssDNA and for A3 enzymes (orange) to access the ssDNA, they must be able to compete with RPA. The ssDNA mutagenesis during transcription can take place only if the lesions in the non-transcribed strand persist until DNA replication, then they can be fixed into mutations by TLS. By contrast, resolution of the R-loops provides the undamaged template for excision repair and prevents mutagenesis. For the mutagenesis associated with both DSB and BIR, there is no template for accurate excision repair. An A3 monomer is shown, although A3B forms larger oligomers and A3H is a dimer. Only A3A is monomeric.