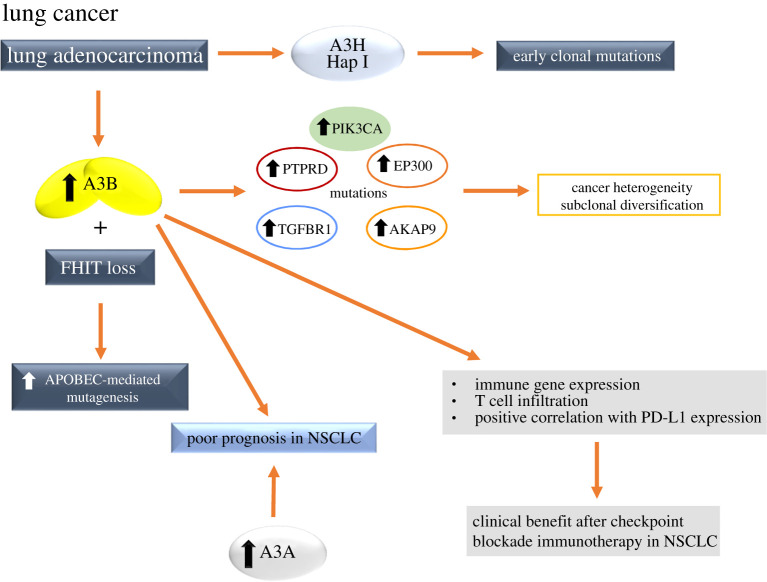
Figure 4.
Causes and effects of A3 upregulation in lung cancer. Mutations within an A3B context were found in driver genes such as PTPRD, PIK3CA, EP300, TGFBR1 and AKAP9, fuelling cancer heterogeneity and subclonal diversification. In lung adenocarcinoma, A3H Hap I expression was associated with early clonal mutations and increased A3B expression and the loss of FHIT protein expression was associated with higher levels of APOBEC-mediated mutagenesis. The overexpression of both A3B and A3A is associated with poor clinical outcomes in NSCLC patients, but A3B overexpression also predicts clinical benefit after checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in patients. For more details, see §5.2.