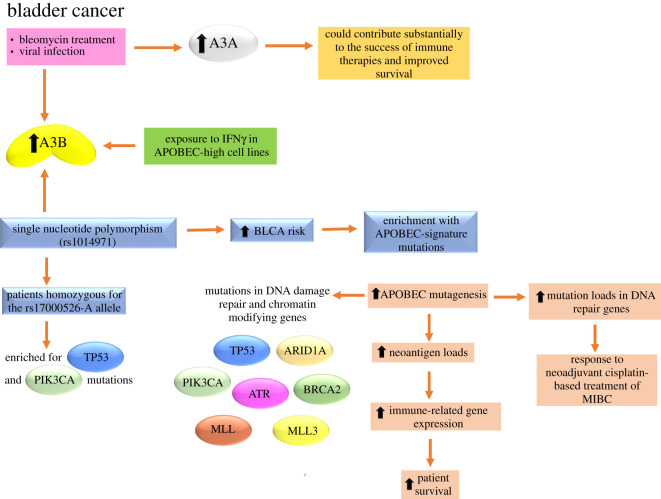
Figure 5.
Causes and effects of A3s upregulation in BLCA. The expression of both A3A and A3B can be induced by bleomycin, a DNA-damaging agent and by an RNA virus that induces an IFN response. Also, the direct exposure to IFNγ in APOBEC-high cell lines increases the A3B expression. Hypermutation in BLCA (mainly by A3A) could contribute substantially to the success of immune therapies and improved survival. The single nucleotide polymorphism, rs1014971, was associated with BLCA risk, increased A3B expression and enrichment with APOBEC-signature mutations in bladder tumours. The tumours from patients homozygous for the rs17000526-A allele were enriched for TP53 and PIK3CA mutations. Increased APOBEC mutagenesis in BLCA patients have a positive association with neoantigen loads, the relative abundances of immune-related genes and the improved survival. Also, increased mutation loads, especially in DNA repair genes, were associated with a response to neoadjuvant cisplatin-based treatment of MIBC. Tumours enriched for APOBEC mutagenesis had better survival and were more likely to have mutations in both DNA damage repair and chromatin-modifying genes such as TP53, PIK3CA, ATR, BRCA2, MLL, MLL3 and ARID1A. For more details, see §5.3.