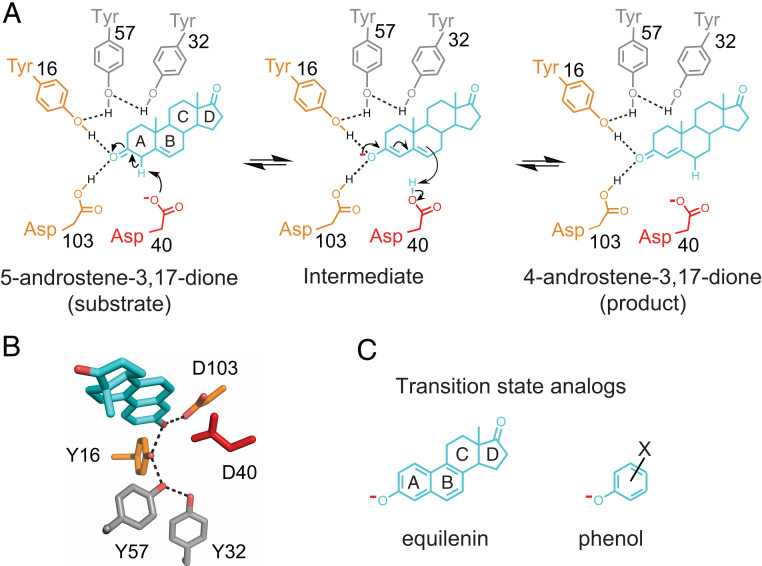
Fig. 1.
The KSI reaction. Reaction mechanism and schematic depiction of the active site (A) and its 3D organization (B) [PDB ID code 1OH0 (87)]. KSI catalyzes double bond isomerization of steroid substrates (shown for the substrate 5-androstene-3,17-dione) utilizing a general acid/base D40 (which we refer to herein as a general base, for simplicity), and an oxyanion hole composed of the side chains of Y16 and D103 (protonated); general base and oxyanion hole residues are colored in red and orange, respectively. The product in A, 4-androstene-3,17-dione, is the substrate of the reverse reaction and was used for RT X-ray crystallography herein. (C) Examples of oxyanion KSI TSAs used for the KSI TSA ensembles: Equilenin (Left) and a substituted phenolate (Right).