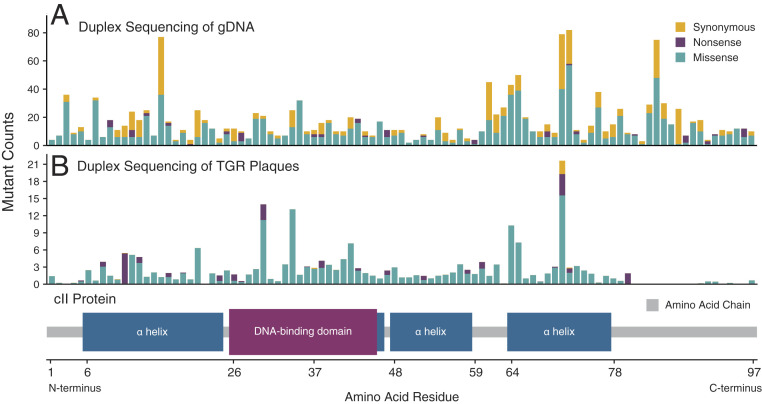
Fig. 3.
DS is agnostic to reporter gene function, whereas the TGR assay counts only phenotypically selectable mutations. (A) The distribution of all mutations identified by DS of cII from genomic DNA across all Big Blue tissues and treatment groups is shown by codon position and functional consequence. (B) The same analysis is presented for mutations identified from individually collected mutant plaques. Whereas DS recovers all functional classes of predicted amino acid mutations along the entire gene, mutations from picked mutant plaques that have lost a functional cII protein are devoid of synonymous variants and mutations at the nonessential C and N termini. Nucleotide positions with higher than average mutation counts by DS reflect mutagenic hotspots. The different mutation profile observed in the TGR plaque sequencing is more reflective of which sites are most phenotypically selected.