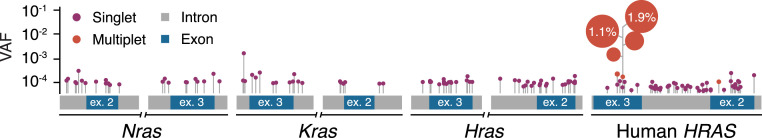
Fig. 8.
Early neoplastic evolution in cancer-prone mice following carcinogen exposure. The location and variant allele frequency (VAF) of SNVs are visualized across the genomic intervals for the introns and exons captured from the endogenous mouse Ras family of genes as well as the human transgenic HRAS loci from the Tg-rasH2 mouse model. Singlets are mutations identified in a single molecule of a sample. Multiplets are an identical mutation identified within multiple molecules within the same sample and may represent a clonal expansion event. Pooled data from all tissues in the experiment (lung, spleen, and blood) are included. The height of each point (log scale) corresponds to the VAF of each SNV. The size of the point corresponds to the number of counts observed for the mutant allele. A cluster of multiplet A∙T→T∙A transversions at the human oncogenic HRAS codon 61 hotspot is seen in four out of five urethane-exposed lung samples and one out of five urethane-exposed splenic samples (SI Appendix, Table S4). The observation of an identical mutation in independent samples with high-frequency multiplets in a well-established cancer driver gene likely indicates positive selection. Notably, these clones are defined by the transversion A∙T→T∙A in the context NTG which is characteristic of urethane mutagenesis.