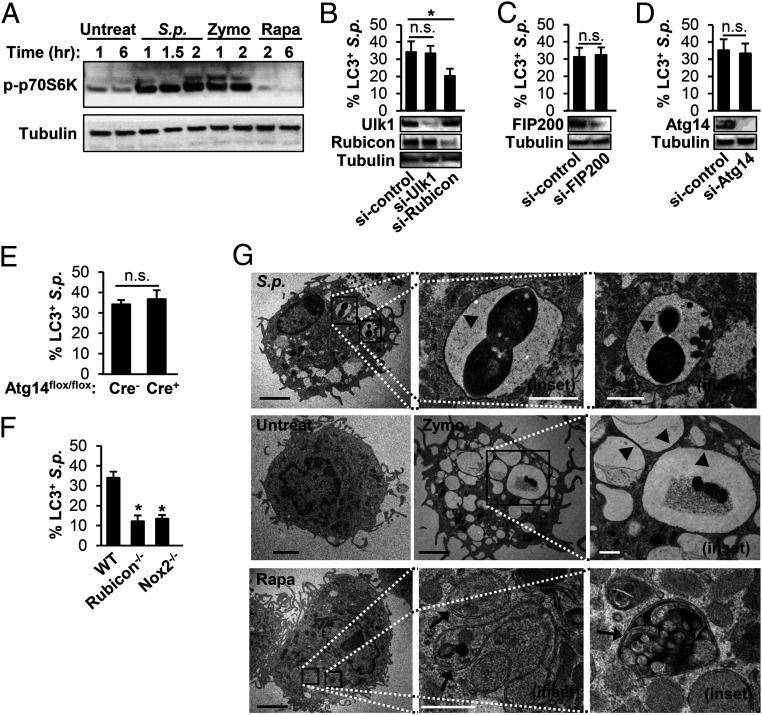
Fig. 3.
S.p. triggers LAP and not canonical autophagy in primary murine BMDMs. (A) BMDMs from WT mice were untreated, infected with S.p., or treated with 10-μg/mL Zymo or 200-nM Rapa for the indicated periods. Cell lysates were immunoblotted to detect p-p70S6K and tubulin. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (B–D) RAW264.7 macrophages stably expressing GFP-LC3 were transfected with control siRNA, Ulk1 siRNA, or Rubicon siRNA (B); control siRNA or FIP200 siRNA (C); control siRNA or Atg14 siRNA (D) for 48 h. These cells were treated with S.p. Cell lysates were immunoblotted to detect Ulk1, Rubicon, FIP200, Atg14, or tubulin. The percentage of LC3+ S.p. was quantified. *P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test. (E and F) BMDMs isolated from Atg14-KO (Atg14flox/flox-LysM-Cre+) or control (Atg14flox/flox-LysM-Cre−) mice (E); WT, Rubicon−/−, and Nox2−/− (F) were transfected with GFP-LC3 and then were infected with S.p. for 1 h. The percentage of LC3+ S.p. was quantified. Data shown mean ± SEM from one representative experiment from, at least, two independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 by the Mann–Whitney U test. n.s.. (G) BMDMs were untreated or infected with S.p. for 40 min or treated with 10-μg/mL Zymo for 40 min or 200-nM Rapa for 6 h and subjected to transmission electron microscopy. Images are representative of three experiments. Arrowheads indicate single membrane; arrows indicate double membrane. The magnified insets represents the area indicated by the squares. (Black scale bar: 2 µm; white scale bar: 500 nm.) n.s., not significant; S.p., Streptococcus pneumoniae.