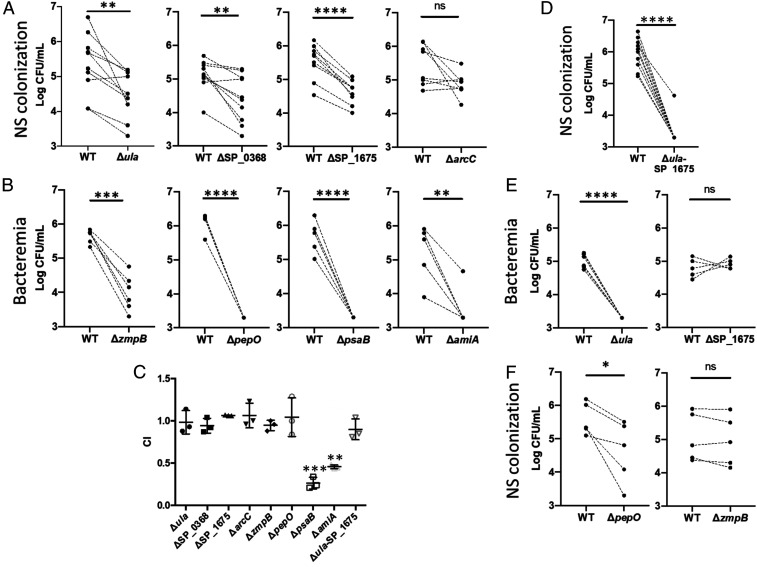
Fig. 6.
In vivo competition experiments between pneumococcal strain TIGR4 and isogenic mutants in highly expressed genes. Mutants were tested using a completive index assay against WT TIGR4. Paired WT and mutant samples are denoted by dots with a connecting dashed line. (A) Bacterial titers in nasal lavage fluid of colonized mice 5 d postinoculation with WT TIGR4 and Spn deficient in genes highly expressed in the nasopharynx. (B) Bacterial titers in the blood of mice 1 d after intratracheal with WT TIGR4 and Spn deficient in genes highly expressed during invasive disease. (C) Mutants tested in A and B were tested for overall fitness in Todd-Hewitt broth with 0.5% yeast extract (THY). Competitive index values were calculated by dividing the numbers of CFU for the isogenic mutants by those for WT. (D) A double mutant, deficient in both ula and SP_1675 was tested versus TIGR4 WT in the nasopharynx model of colonization. (E) Cross infection experiments in which genes highly expressed in nasopharynx (Δula and ΔSP_1675) were tested in the model of lower respiratory tract infection with bacteremia. (F) Genes highly expressed in disease anatomical sites (ΔpepO and ΔzmpB) were tested with the nasopharynx model of colonization. For all panels, mutants were compared to WT using a paired Student’s t test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; ns, not significant).