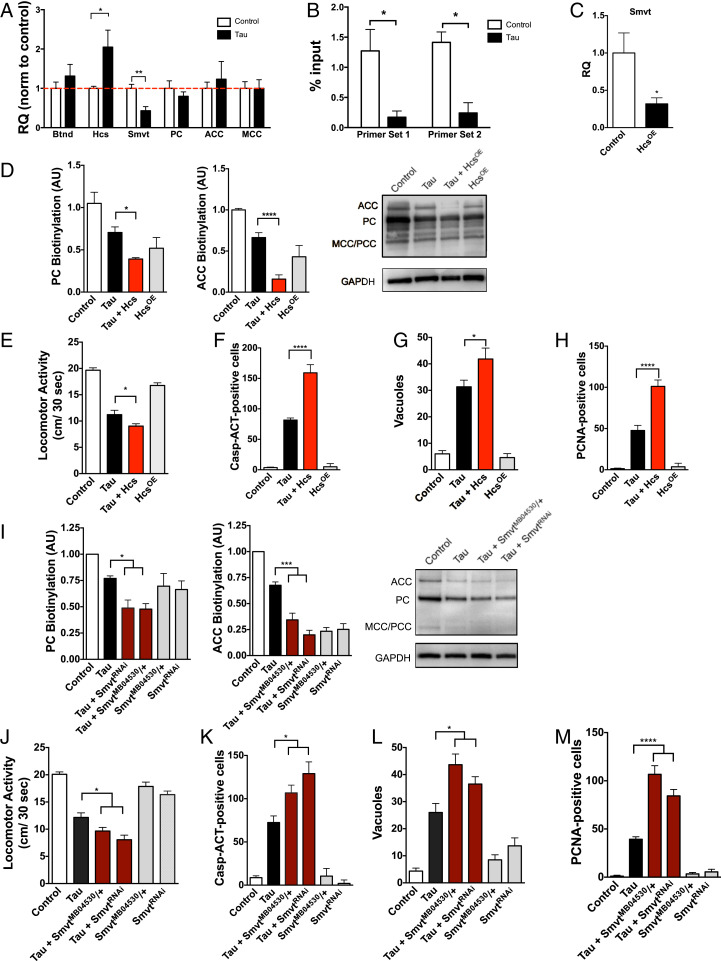
Fig. 4.
Human tauR406W transgenic flies show aberrant changes in expression of biotin-related genes. (A) TauR406W transgenic flies have a significant increase in holocarboxylase synthetase (Hcs) and a decrease in sodium multivitamin transporter (Smvt) level as shown by qPCR. (B) TauR406W transgenic flies have reduced H3K9me2 at the Hcs locus as shown by ChIP-qPCR (C). Overexpression of Hcs reduces Smvt expression in fly heads. Hcs overexpression further reduces carboxylase biotinylation (D), enhances tauR406W-mediated behavioral deficits (E) and neurotoxicity as shown by caspase activation, vacuole formation, and cell-cycle reentry (F–H). Similarly, reductions in Smvt (SmvtRNAi or SmvtMB04530/+) reduce carbozylase biotinylation (I) and enhance tauR406W-mediated behavioral deficits, caspase activation, vacuole formation, and cell-cycle reentry (J–M). n = 6 per genotype. For A–C, t test was used for analysis, and in D–M, ANOVA was used for analysis. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Control genotype (A–E, G–J, L, M): elav-GAL4/+. Control genotype (F and K): elav-GAL4/+;UAS-CD8-PARP-Venus/+.