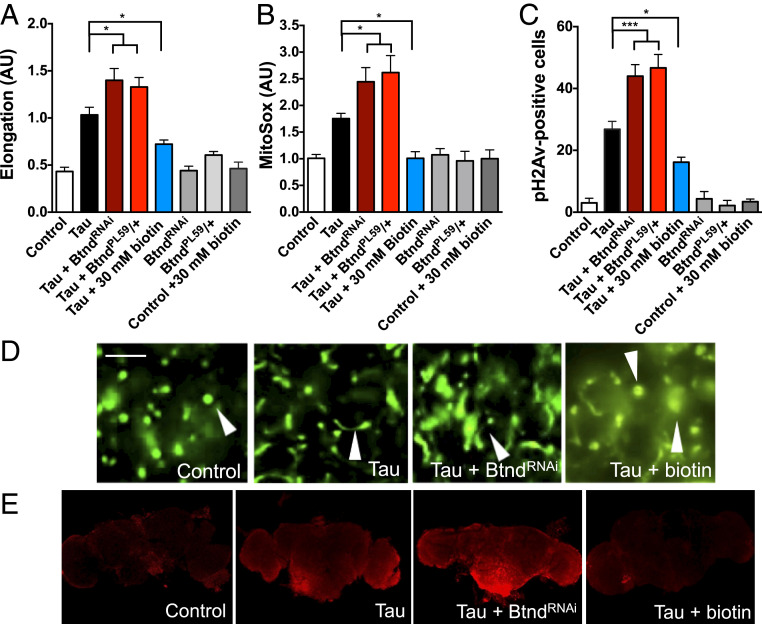
Fig. 5.
Biotin status modifies mitochondrial morphology and function in human tauR406W transgenic flies. (A) Reduced biotinidase enhances tauR406W-mediated mitochondrial elongation, while biotin feeding rescues this abnormal mitochondrial morphology. n = 6 per genotype. (B) Reduced biotinidase enhances tauR406W-mediated superoxide formation, while biotin feeding rescues this abnormal mitochondrial function. n = 10. (C) Reduced biotinidase enhances DNA damage compared to tauR406W transgenic flies, while biotin feeding rescues this damage as shown by immunohistochemical quantification of pH2Av-positive cells. n = 6. (D) Representative images of GFP-tagged mitochondria quantified in A. Arrowheads highlight representative mitochondrial morphology. (Scale bar, 5 μm.) (E) Representative Z-stacks of superoxide dye MitoSox used in B (Imaged at 10× magnification). A–C were analyzed by ANOVA. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. Control genotype (A and D): elav-GAL4/+;UAS-mito-GFP/+. Control genotype (B, C, E): elav-GAL4/+.