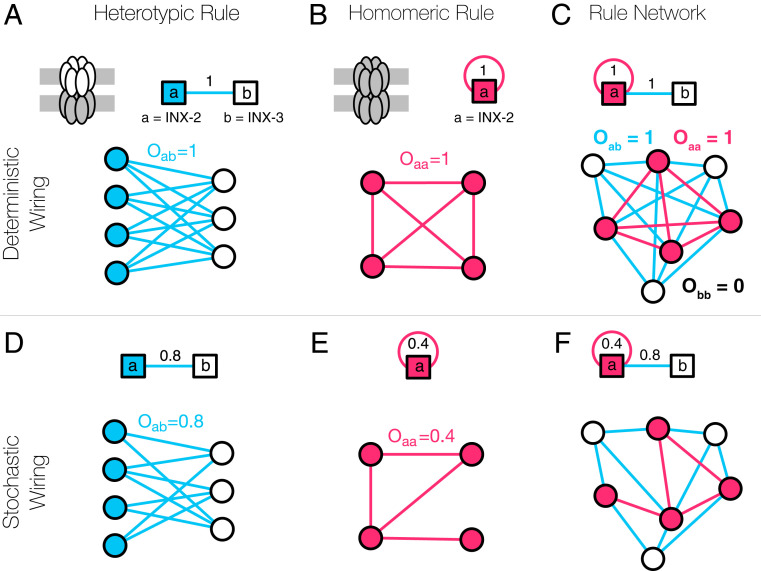
Fig. 3.
GJs in the CM. GJs are formed by interacting hemichannels comprising innexin proteins. In the simplest case, a hemichannel is made of a single innexin, meaning that the expressed innexins can directly serve as labels. (A) Two Drosophila innexin proteins, inx-2 and inx-3, have been found to form (heterotypic) GJs, resulting in multiple potential neural connections (41). (B) There is evidence that inx-2 can form homomeric GJs, establishing connections between the neurons expressing inx-2, represented by the self-loop in the figure. (C) Altogether, the two rules (A and B) can be integrated into a rule network that serves as a genetic template for the GJ connectome. (D) The formalism behind the CM allows for stochastic rules, that is, a weight of 0.8 indicates that of the potential neural connections are present in the brain. This stochasticity can arise from multiple factors, including noisy or incomplete expression and connectome data, spatial effects, biological constraints, and true stochasticity of neuronal wiring. (E) According to oocyte experiments (51), the homomeric innexin rule of Drosophila inx-2 has a weight of 0.4, as only of the possible links are observed. (F) Even in the presence of apparent or true stochasticity, we can capture the GJ connectome using only a few (weighted) innexin rules.