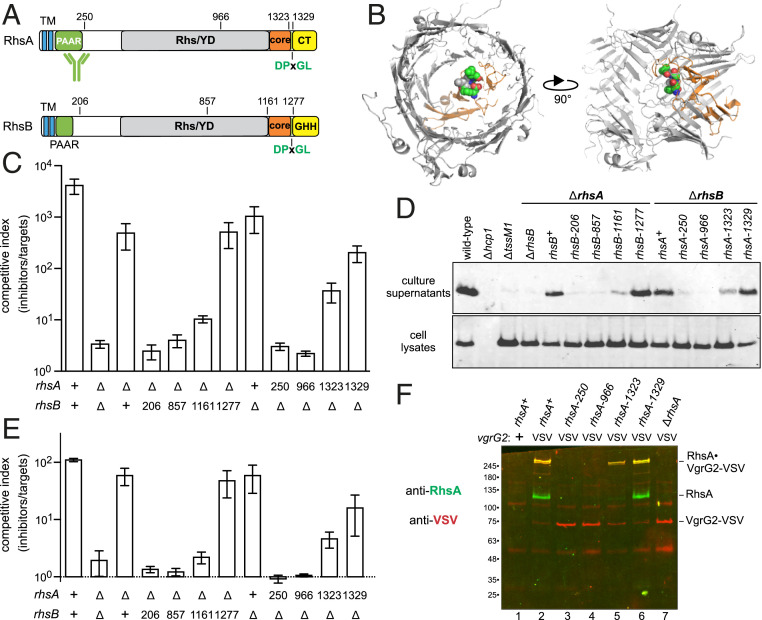
Fig. 4.
Rhs PAAR domains are not sufficient to support T6SS-1 activity. (A) RhsA and RhsB each contain two predicted N-terminal TM helices. The C-terminal toxin domains are delineated by DPxGL peptide motifs within the Rhs-associated core domain. The activity of RhsA-CT is unknown, and RhsB carries a Tox-GHH DNase domain (Pfam: PF15636). (B) Structural model of the RhsA β-cage. The YD-repeat region, core domain, and DPxGL motif are color coded as in A. (C) ECL inhibitor strains were cocultured with E. coli target bacteria at a 1:1 ratio for 4 h. (D) Culture supernatants and cell lysates from the indicated ECL strains were examined by immunoblotting with polyclonal antisera to Hcp1. (E) ECL inhibitor strains were cocultured with ECL ∆tle ∆tli target cells at a 1:1 ratio for 4 h. (F) VgrG2-VSV was immunoprecipitated from indicated ECL strains with anti-VSV agarose. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to RhsA (green) and VSV-G (red).