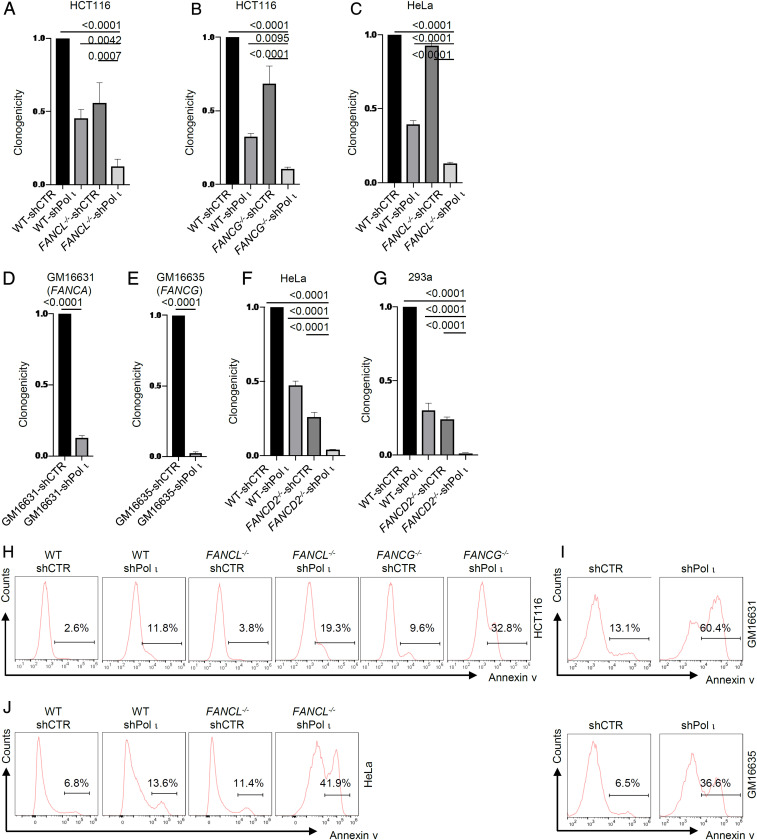
Fig. 2.
Pol ι loss leads to synthetic lethality with FANCL/FANCG/FANCD2 deficiency. (A–C) Clonogenic efficiency of Pol ι shRNA-knockdown HCT116 FANCL−/− cells, FANCG−/− cells, and HeLa FANCL−/− cells. (D and E) Clonogenic efficiency of Pol ι shRNA-knockdown GM16631 and GM16635 patient cells. (F–G) Clonogenic efficiency of Pol ι shRNA-knockdown HeLa FANCD2−/− and 293A FANCD2−/− cells. (H) Flow cytometry histogram of Annexin V-positive cells in HCT116 wild-type (WT), FANCL−/−, and FANCG−/− cells subjected to shRNA-knockdown of Pol ι. (I) Flow cytometry histogram of Annexin V-positive cells in GM16631 and GM16635 patient cells subjected to shRNA-knockdown of Pol ι. (J) Flow cytometry histogram of Annexin V-positive cells in HeLa WT and FANCL−/− cells subjected to shRNA-knockdown of Pol ι.