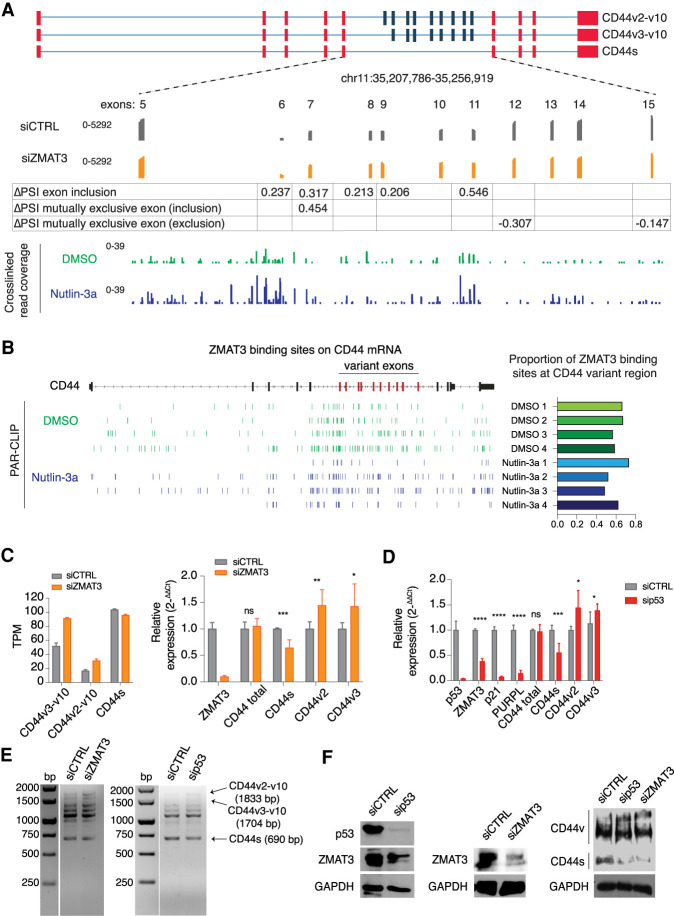
Figure 3.
ZMAT3 or p53 depletion promotes alternative splicing of the CD44 pre-mRNA, resulting in an increased expression of the oncogenic isoforms CD44v2-10 and CD44v3-v10, and decreased expression of the standard isoform CD44s. (A) Schematic representation of some CD44 isoforms, with invariant exons 1–5 and the last four exons colored in red and variant exons 6–10 colored in blue. The bottom track shows RNA-seq coverage from HCT116 cells treated with ZMAT3 or control siRNAs. The increase in PSI of each variant exon upon ZMAT3 silencing is indicated. The bottom track shows the distribution of cross-linked sequence reads from ZMAT3 PAR-CLIP experiments. (B) Genome browser track of ZMAT3 binding sites from all biological replicates across the CD44 gene showing the enrichment of ZMAT3 binding around the variant CD44 exons (left part) and proportion of binding sites at CD44 variant region/CD44 total RNA (right part). (C) Gene expression levels of CD44s, CD44v2-v10 or CD44v3-v10 upon ZMAT3 kd from RNA-seq in transcripts per million (TPM) (left), or RT-qPCR experiments (right). In the case of qPCR, we were only able to measure the expression of all CD44variants harboring v2 or v3 exons. (*) P < 0.05, (***) P < 0.001, (ns) nonsignificant. RT-qPCR values are the average of at least three biological replicates. (D) RT-qPCR quantification of CD44s, CD44v2, CD44v3, and known direct p53 targets (ZMAT3, p21, and the PURPL lincRNA) after p53 kd in HCT116 cells. (*) P < 0.05, (**) P < 0.01, (***) P < 0.001, (****) P < 0.0001, (ns) nonsignificant. RT-qPCR values are the average of at least three biological replicates. (E) Representative images of semiquantitative PCR from HCT116 cells following ZMAT3 or p53 kd. The forward primer was designed on exon 2 and reverse on exon 18 of CD44 mRNA. Bands were Sanger-sequenced to confirm the isoforms. (F) Immunoblots from HCT116 lysates for p53, CD44, ZMAT3, and GAPDH following p53 or ZMAT3 kd.