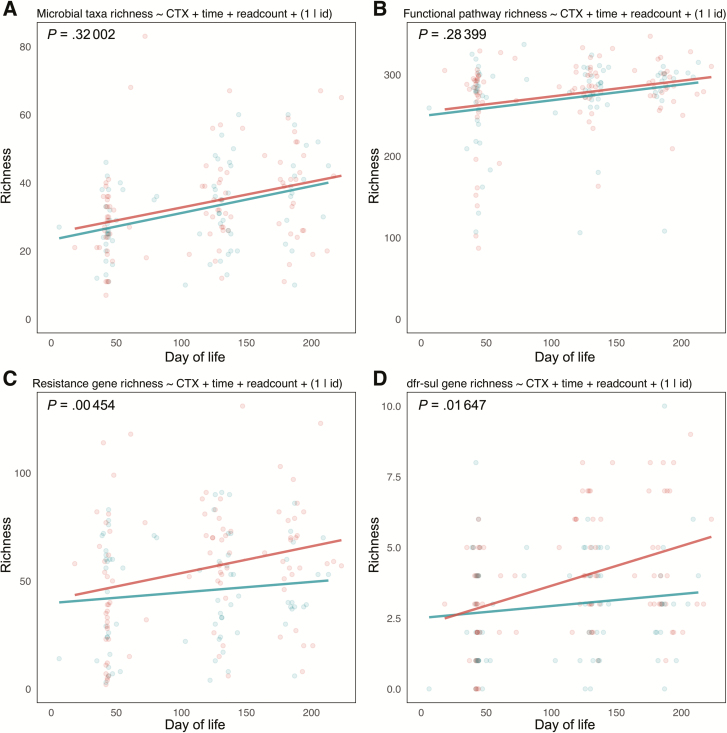
Figure 6.
Resistance gene richness (α-diversity) is significantly higher in cotrimoxazole-treated human immunodeficiency virus–exposed, uninfected (HEU) infants (CTX-T) compared to HEU infants not treated with cotrimoxazole (CTX-N). Points represent individual patient samples colored by treatment group (red for CTX-T infants and blue for CTX-N infants), and lines represent predictions of simple linear regression models for the 2 groups. The x-axis for each plot is the day of life for each infant calculated from their day of birth, and the y-axis is richness. Models were made for microbial taxa (A), functional pathways (B), resistance genes (C), and trimethoprim- and sulfonamide-resistance (dfr/sul) genes (D). Formulas for each linear mixed-effects model are reported above the plots, and these models were compared using likelihood-ratio tests to null models made without the cotrimoxazole treatment variable (CTX) included. The P values for these comparisons of linear mixed-effects models are reported at top left of each graph.