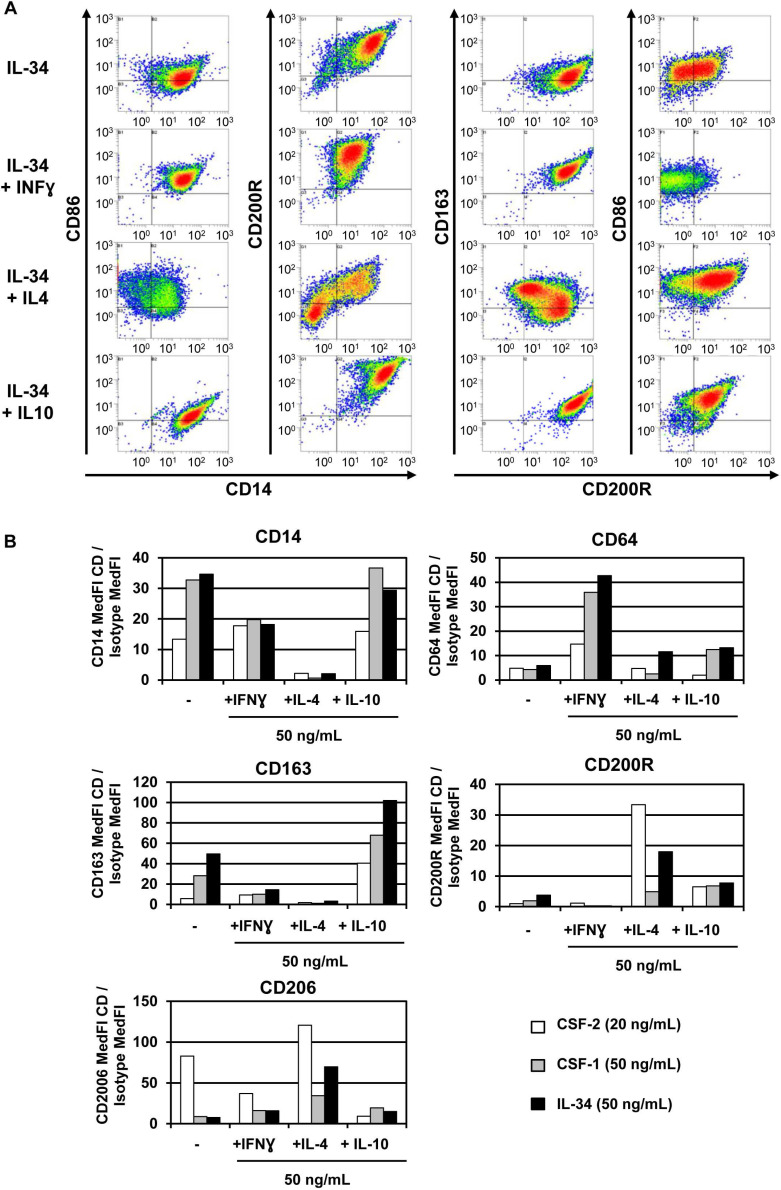
Figure 4.
IL-34 is a pro-M2 macrophage differentiation factor. Macrophage isolation and treatment were performed as described in A) IL-34 treatment induced macrophage differentiation with an M2 phenotype, alone or in combination with IL-4 and IL-10. Macrophages were treated with IL-34 (50 ng/ml) or in combination with IFN-γ (50 ng/ml; pro M1), IL-4 (50 ng/ml; pro M2a), and IL-10 (50 ng/ml; pro M2c), for 2 days and cells were analyzed by means of flow cytometry using specific antibodies for both M1-like macrophages (CD14, CD86 and CD64) and M2-like macrophages (CD163, CD200R and CD206). B) Comparison of macrophage differentiation after treatment with the cytokines CSF-2 (20 ng/ml), CSF-1 (50 ng/ml) and IL-34 (50 ng/ml) alone or in combination with IFN-γ, IL-4 or IL-10 as performed in A. The three cytokines in combination with IFN-γ were able to induce M1 macrophage differentiation as shown by the increase in CD64, an M1 marker. IL-34 modulates M2 markers (CD163, CD200R and CD206) alone or in combination with IL-4 and IL-10. No effect of IL-34 was observed in CD14 expression. Overall, IL-34 was able to induce M1 and M2 macrophage differentiation with a specific increase in CD163, an M2 marker.