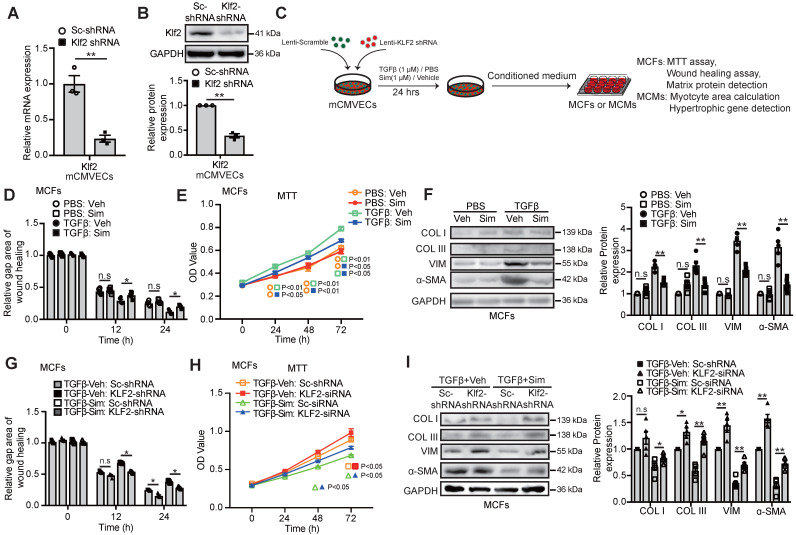
Figure 4.
Endothelial KLF2 mediates the inhibitory effects of simvastatin on TGFβ stimulated cardiac microvasculature endothelial cells condition medium (mCMVEC-CM) enhanced migration, proliferation and fibrotic gene expression of cardiac fibroblasts. A-B, Klf2-shRNA significantly reduces the Klf2 expression in mCMVECs by RT-qPCR (A) and western blot (B) compared with scramble (sc)-shRNA treatment (n=3). C, Schematic diagram of an in vitro experiment to investigate the interaction between mouse cardiac microvascular endothelial cell line (mCMVECs) and mouse cardiac fibroblast (MCFs) or mouse cardiomyocytes (MCMs). D-F, The simvastatin treated mCMVEC-CM significantly inhibits migration of cardiac fibroblasts by wound healing assay (D), proliferation by MTT assay (E), and reduces their expression of α-SMA, and collagen I, III by western blot (F) compared with the vehicle treated mCMVEC-CM upon TGFβ stimulation, while no significant changes is observed in mCMVECs between simvastatin and vehicle treatment upon PBS stimulation (n=5). G-I, CM from Klf2-shRNA knockdown mCMVECs attenuates the simvastatin-mediated inhibition of increased migration of cardiac fibroblasts by wound healing assay (G), proliferation by MTT assay (H) and the simvastatin-mediated reduced expression of α-SMA, collagen type I, III by western blot (I) (n=5). Data are means ± S.E.M. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and n.s not significant. Unpaired Student's t-test (A, B) and 2-way ANOVA with Turkey test (D-I).