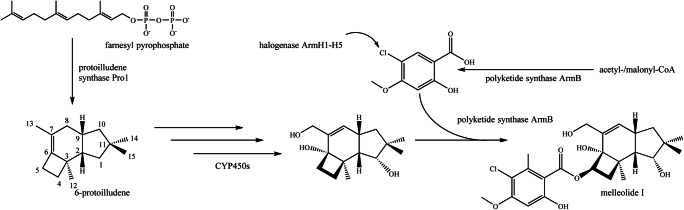
Fig. 2.
The melleolide I biosynthesis pathway. The pathway begins with the cyclization of farnesyl diphosphate to 6-protoilludene (Engels et al. 2011) and then oxygenation catalyzed by cytochrome P450 monooxygenases. The final step is the attachment of an orsellinic acid, produced, and transferred by the polyketide synthase ArmB (Lackner et al. 2013). Subsequent chlorination of the side chain is carried out by halogenases ArmH1–ArmH5 (Wick et al. 2016). In contrast to the main metabolite melleolide I, the structures of armillyl orsellinate and armillane (Bohnert et al. 2011) differ in the presence/absence or position of the double bond in the six-ring system and the number and position of hydroxyl groups