Fig. 9.
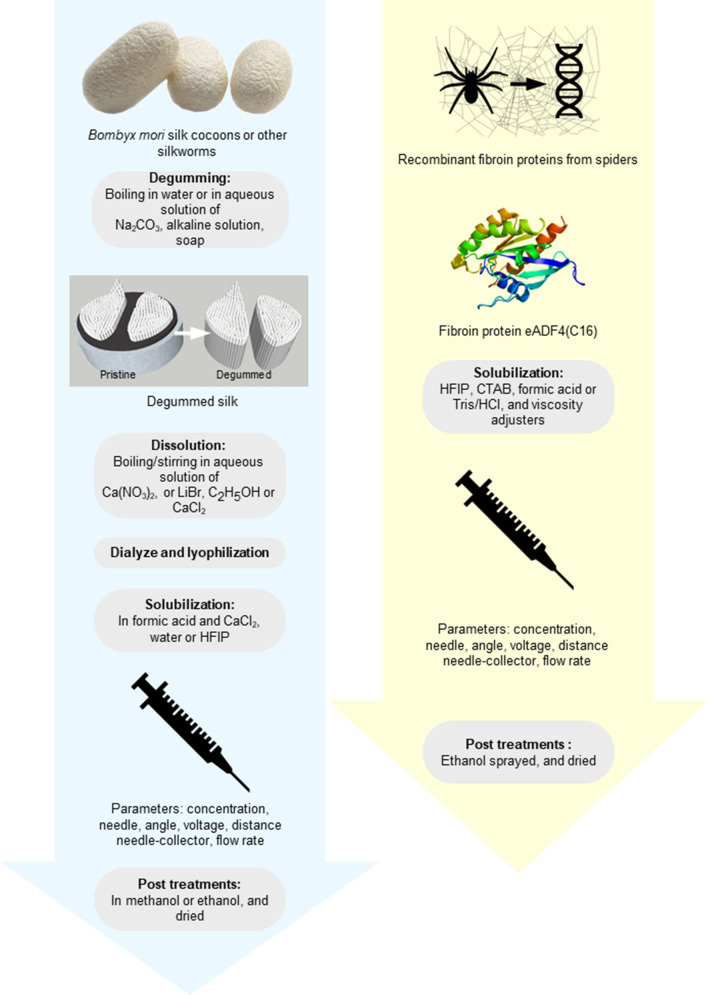
Protocols for solubilization of silk proteins from silkworms (left) and spidroins (right). Degumming and dissolution of silk are necessary for silkworm cocoons, and very rarely observed in spider think electrospinning, as the proteins are obtained from recombinant spider silk instead of natural fibers (Table 3). Degumming consists of washing the sericin off the silkworm’s silk often achieved in an alkaline detergent solution, sericin being a glue-like protein with little biocompatibility (Altman et al. 2003). Solvents used for preparation of the spinning dope vary depending on the type of silk: for silkworm’s silk, the solvent can be formic acid or HFIP (Table 3), but biomedical applications prefer water, for spider’s silk, the organic solvent HFIP is the most used, but DeSimone et al. suggested an aqueous spinning dope based on the use of Tris/HCl (DeSimone et al. 2020). Post-treatments include vaporization or bath of methanol, water or ethanol (Min et al. 2004; Lang et al. 2013),