Fig. 7.
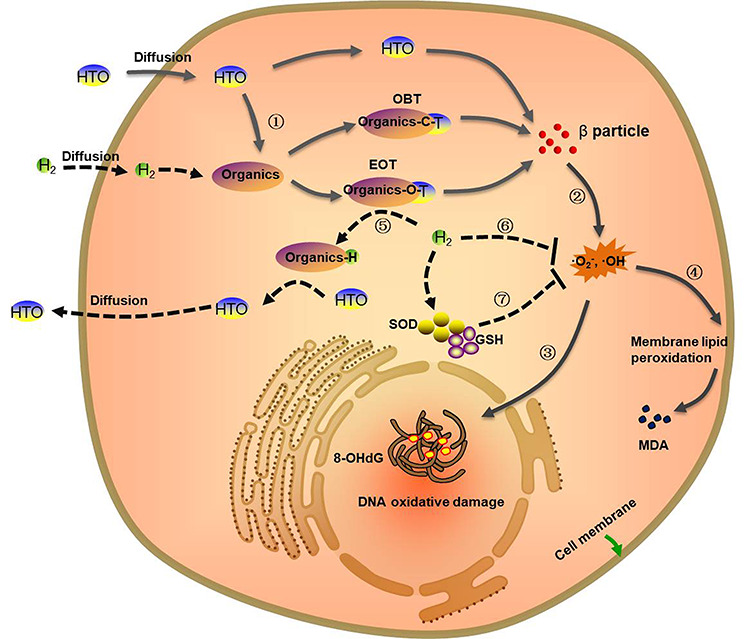
Mechanism of HRW in the attenuation of the radiotoxicity induced by tritium exposure. The solid arrow represents the damage mechanism of HTO in cells. The dotted arrow represents the mechanism of HRW for tritium excretion and treatment. ①The HTO entering the organism is bound to organic molecules to form OBT and EOT. ②The beta particles emitted by OBT, EOT and free HTO induce an increase in intracellular ROS, such as •OH and O2•-, through radiolysis of H2O and oxidation of biomolecules. ③The excess ROS results in DNA oxidative damage and products 8-OHdG. ④The free radicals also lead to membrane lipid peroxidation to destroy the biofilm structure and products MDA. ⑤HRW with a high concentration of hydrogen competitively binds to the binding sites of tritium in organics to facilitate the free or weakly bonded tritium diffusing out of cells through isotope exchange. ⑥The antioxidant activity of HRW can neutralize excess free radicals (•OH, O2•-). ⑦The exhaustion of cellular endogenous antioxidants (GSH and SOD) stimulated by ROS can also be reversed by HRW, resulting in the relief of oxidative stress injury.
