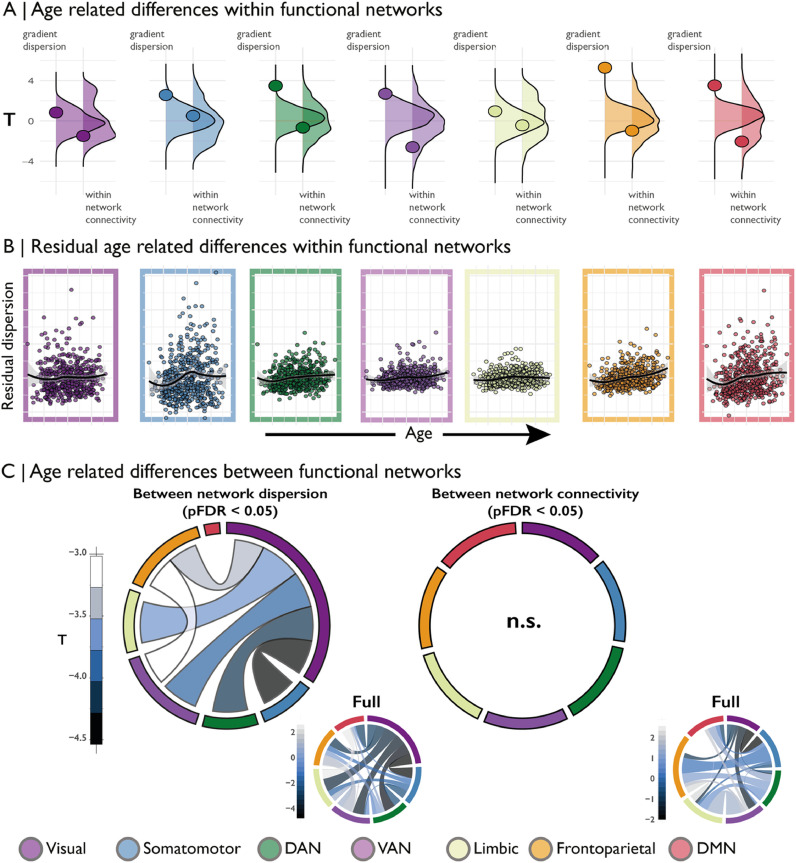
Fig. 2.
(A) Age-related difference (t-statistic) in within network dispersion and within network connectivity for each Yeo network. Underlying density plots show the null distributions of t-statistics derived from spin permutations. Positive t-values signify increased network dispersion with age. (B) Residuals of the dispersion model (including controls for sex, motion and within network connectivity) against age residuals for the same model for each Yeo network. (C) Between network dispersion and between network connectivity. Network borders are scaled according to the size of the total effect from that community (e.g. the visual network is largest in the left panel as most significant between network dispersion involves the visual network). Insert panels on the right show the full between network pattern for all connections including non-significant ones.